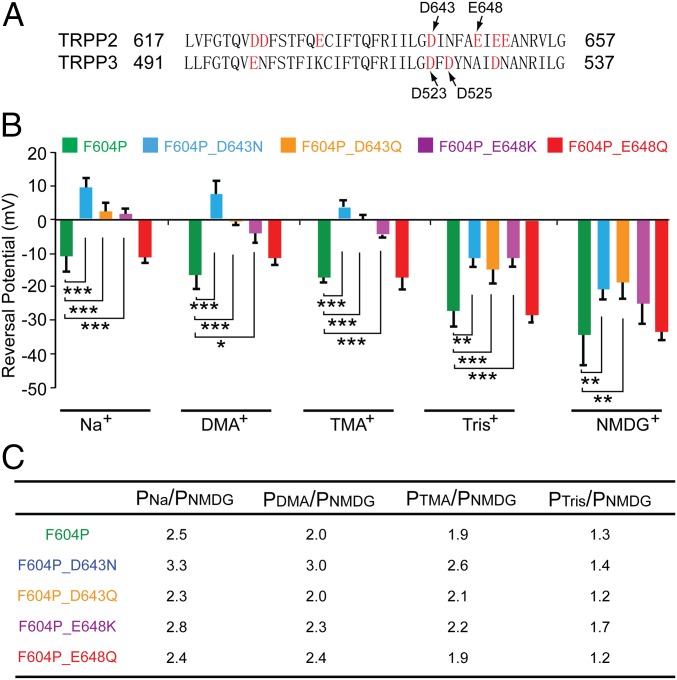
Fig. 4.
D643 is critical for the ion selectivity of the TRPP2 channel. (A) Sequence alignment of the putative pore regions of human TRPP2 and TRPP3. Arrows indicate the two amino acids that are crucial for ion selectivity of the TRPP3/PKD1L3 channel (Bottom) and the two amino acids of TRPP2 that were mutated in this study (Top). (B) Bar graph showing the reversal potentials of currents recorded from TRPP2_F604P (green bars), F604P_D643N (blue bars), F604P_D643Q (orange bars), F604P_E648K (purple bars), and F604P_E648Q (red bars) in bath solutions containing 100 mM Na+, DMA+, TMA+, Tris+, or NMDG+. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (C) Relative permeability ratios of indicated ions to NMDG+ in listed TRPP2 mutants. We chose NMDG+ as the reference ion because its permeability has the smallest change among all ions when different mutants were tested. However, it should be noted that because the NMDG+ permeability itself was increased in three of the four mutants, the permeability changes of other ions caused by these mutations are underestimated if one just compares the numbers in the table. More detailed results on the changes of both reversal potential and relative permeability ratios are listed in Table S1.