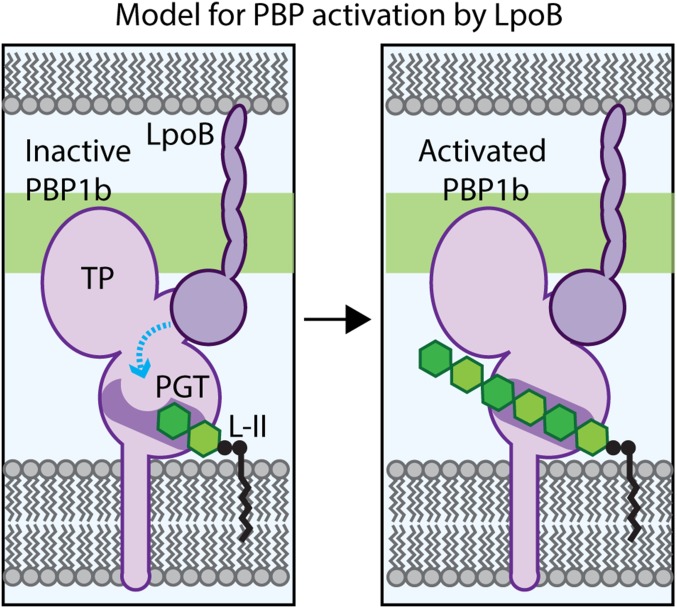
Fig. 5.
Model for PBP1b regulation by LpoB. Shown is a schematic of the E. coli cell envelope with the inner membrane (Bottom) and partial outer membrane (Top) bracketing the PG layer (green). (Left) PBP1b is depicted in an inactive conformation, with the active site channel occluded in part by residue E313, such that the lipid-II (L-II) substrate cannot be elongated. We propose that the LpoB binding to the UB2H domain induces a conformational change in PBP1b (blue line) to alter the PGT active site, such that the channel opens (Right) to allow for lipid-II polymerization by the PGT domain and eventual crosslinking into the matrix by the TP domain.