Figure 1.
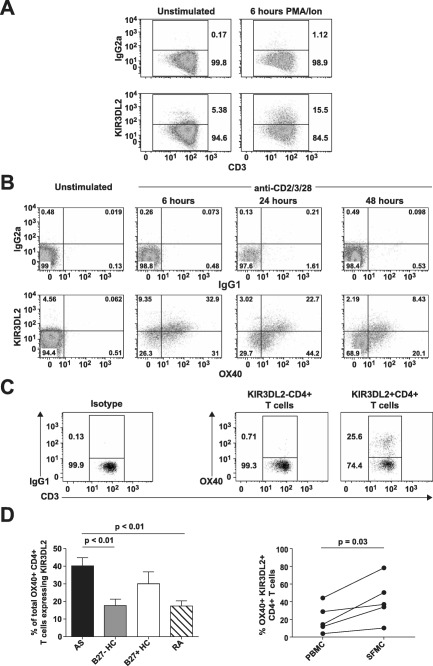
Expression of killer cell immunoglobulin‐like receptor 3DL2 (KIR‐3DL2) is induced upon CD4+ T cell activation, and KIR‐3DL2 expression is correlated with T cell activation in patients with spondyloarthritis (SpA). A and B, Flow cytometry plots show staining of purified CD4+ T cells from a healthy control (HC) for the expression of KIR‐3DL2 before and 6 hours after stimulation with phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) and ionomycin (Ion) (A) or the expression of KIR‐3DL2 and OX40 before and 6, 24, or 48 hours after stimulation with anti‐CD2/CD3/CD28 beads (B). Representative results from 1 of 3 independent experiments are shown. C, Flow cytometry plots show staining for the expression of OX40 on peripheral blood KIR‐3DL2− or KIR‐3DL2+ CD4+ T cells from a patient with ankylosing spondylitis (AS). IgG1 and IgG2a antibodies were used as isotype controls in the flow cytometry analyses. D, The percentage of OX40+CD4+ T cells expressing KIR‐3DL2 was determined in the peripheral blood from patients with AS (n = 15), B27− healthy controls (n = 15), B27+ healthy controls (n = 8), and patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (n = 9) (left) or in matched peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) and synovial fluid mononuclear cell (SFMC) samples from 5 patients with SpA (right). Values are the mean ± SD. P values were determined by analysis of variance.
