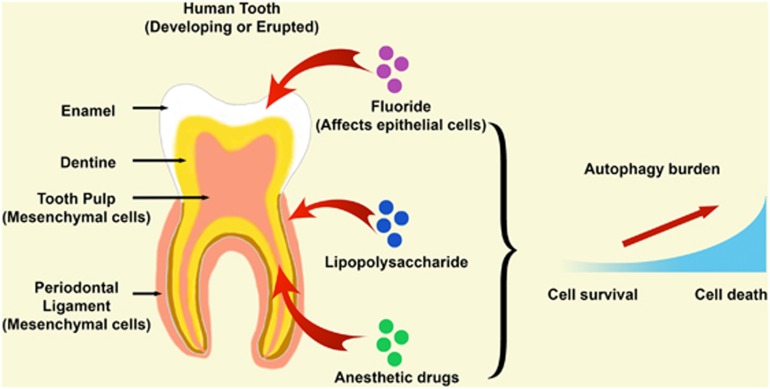
Figure 1.
Current knowledge about autophagy induction by extrinsic factors in dental tissues. In a human tooth, autophagy has been shown to be elevated under different conditions, such as in fluorosis, in periodontal diseases (through lipopolysaccharide) and during local anesthetic treatment. The affected tooth cells can be of epithelial or mesenchymal origin depending on the specific condition and location where one factor acts (illustrated by red arrows). The role of autophagy in a tooth cell can be protective or to induce cell death, which is time and dose dependent