Fig. 2.
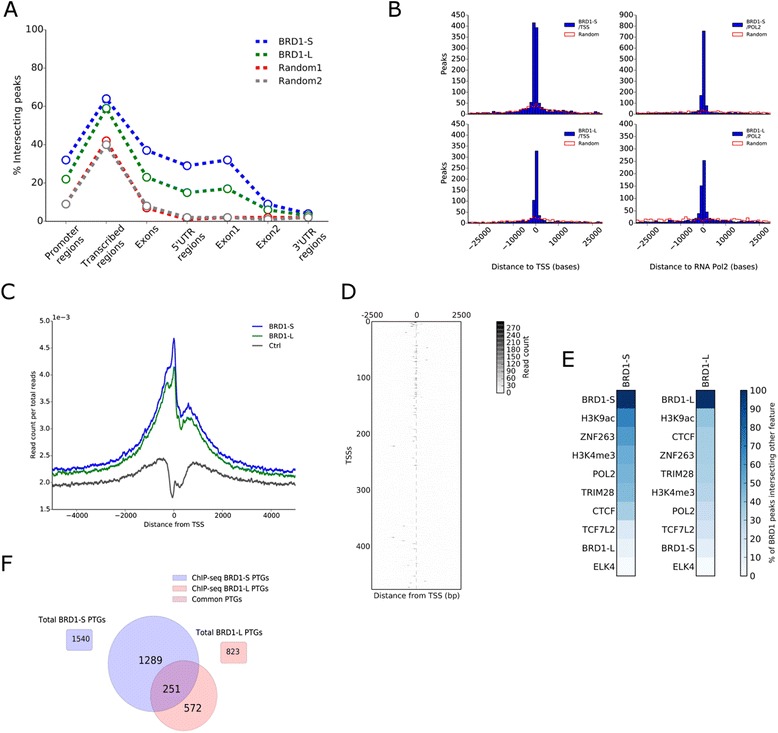
ChIP sequencing analysis of BRD1-S and BRD1-L. a The percentages of BRD1-S and BRD1-L ChIPseq peaks that intersect promoter regions of protein-coding genes (defined as 5 kb upstream from transcription start site), transcribed regions (all exons, introns, and UTRs), exons (all exons), 5’UTR, exon 1 exon 2, and 3’UTR, were identified and shown by the perforated blue and green lines in the graph. Random peak regions, comprising the same chromosome distribution and region sizes as the BRD1 ChIPseq regions, were generated and shown as Random 1 (2205 regions, red) and Random 2 (1722 regions, gray). b The minimum relative distance from a BRD1-S and BRD1-L ChIP-seq region to transcription start sites (left panel) or to RNA Pol II binding sites (right panel) was identified for all 2205 (BRD1-S) and 1722 (BRD1-L) regions and illustrated as the blue histograms. Random peak regions comprising the same chromosome distribution and region sizes as the BRD1 ChIPseq regions were generated and shown as red line histograms (Random). c In order to generate a profile of BRD1-S (blue), BRD1-L (green) binding to the TSS of genes, we identified and plotted the number of sequenced reads per total reads across a window of +/– 5 kb from the TSS of all protein-coding genes in the human genome. The control (Ctrl, black) represents ChIP-seq using an antibody against the HA-epitope. d A heatmap of read counts from BRD1-S ChIP-seq across a +/– 2.5 kb window from the TSS of genes located on chromosome 1 and 10. Only regions with high read counts are shown here. e ChIPseq regions of chromatin-binding proteins and histone marks, identified in HEK293 cell lines, were obtained from the ENCODE database and from a histone H3K9ac dataset [59]. The percentages of BRD1-S and BRD1-L ChIPseq peak regions that intersected with the binding of other chromatin-binding proteins or the location of histone marks were identified and illustrated as heatmaps. f Genes comprising transcription start sites in a window of +/– 5 kb from a BRD1-S or BRD1-L ChIP-seq peak region were identified as promoter target genes (PTGs). Venn diagram illustrates the number of PTGs identified for BRD1-S and BRD1-L
