Fig. 5.
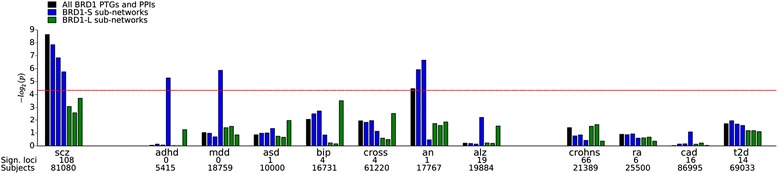
Disease risk gene analysis of the BRD1 network. Enrichment for genetic disease risk was investigated for seven BRD1 sub-networks across 12 GWASs comprising eight brain disorders and four disorders that are not considered brain disorders. The bars indicate BRD1 sub-networks in the order: all BRD1-S and BRD1-L PTGs and PPIs (black), BRD1-S PTGs and PPIs, BRD1-S PTGs, BRD1-S PPIs, BRD1-L PTGs and PPIs, BRD1-L PTGs, and BRD1-L PPIs. GWAS from the left are: schizophrenia (scz) [4, 32], attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (adhd) [27, 32], major depressive disorder (mdd) [28, 32], autism spectrum disorder (asd) [32], bipolar disorder (bip) [30, 32], psychiatric cross-disorders (cross) [25, 32], anorexia nervosa (an) [23, 32], Alzheimer’s disease (alz) [24, 37], Crohn’s disease (crohns) [36], rheumatoid arthritis (ra) [29, 33], coronary artery disease (cad) [31, 34], and type 2 diabetes (t2d) [26, 35]. The red line indicates P = 0.05, before correction for the number of GWAS tested. The number of significant loci as well as the number of subjects in each study is noted under each study
