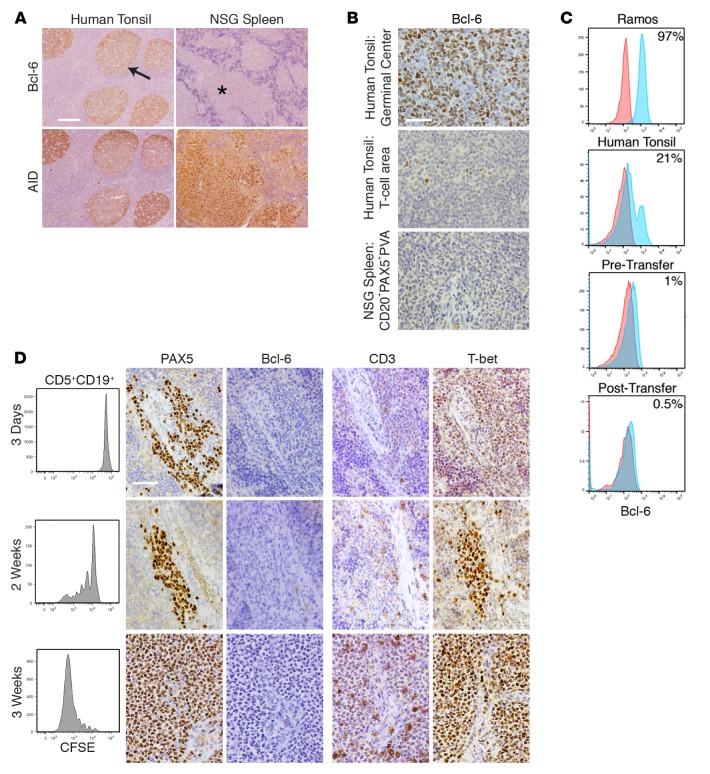
Figure 5. CLL B cell diversification and differentiation occurs without appreciable levels of Bcl-6 protein but in the presence of increasing levels of T-bet protein.
(A) Bcl-6+ cells are rarely found in CD20+PAX5+PVAs and are found less than in tonsillar T cell areas. Human tonsil shows Bcl-6+ cells within germinal centers (GCs) (arrow), whereas chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells within CD20+PAX5+PVAs (*) are Bcl-6–. Conversely, AID+ cells are found on serial sections in both tissues. Scale bar: 250 μm. (B) High-power views of Bcl-6 staining in tonsillar GC, tonsillar T cell area, and xenografted CLL cells within CD20+PAX5+PVA. Scale bar: 50 μm. For A and B, representative data of mice sampled from 13 independent experiments. (C) Representative FC indicates that ≤1% Bcl-6+ cells are found among CD5+CD19+ cells before and after xenografting. This is compared with Ramos cells and from human tonsil cells (CD19+ only). Data are representative of 7 CLL samples analyzed pretransfer and 5 independent xenograft experiments sampling 41 mice. (D) Bcl-6 production does not appear/change upon commencement of B cell division. In contrast, T-bet expression within CD20+PAX5+PVAs becomes more intense. Analysis of CLL transfers at 3 days, 2 weeks, and 3 weeks. Each shows FC of CFSE-labeled CD5+CD19+ cells with companion IH images for PAX5, Bcl-6, CD3, and T-bet. Representative FC and IH images from 5 mice euthanized at each time point in 2 independent experiments involving U-CLL1122 and M-CLL1164. Scale bar: 50 μm. U-CLL, CLL clone with IGHV sequence differing ≤2% from most similar germline gene; M-CLL, CLL clone with IGHV sequence differing >2% from most similar germline gene; PVA, perivascular aggregate; FC, flow cytometry; IH, immunohistology; NSG, NOD/Shi-scid,γcnull; AID, activation-induced cytidine deaminase.