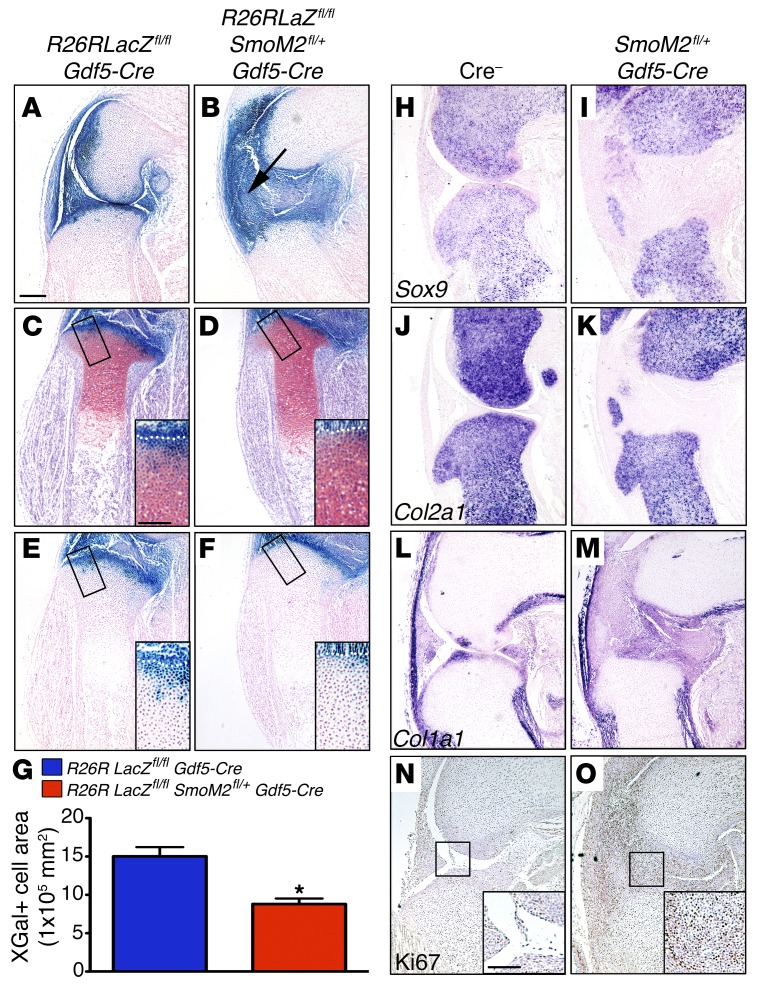
Figure 2. Hedgehog signaling inhibits differentiation of interzone progeny into articular chondrocytes.
(A–F) Hind limb sections from the medial (A and B) or central (C–F) knee stained with X-gal/Nuclear Fast Red (A, B, E, and F) or X-gal/SafO (C and D) of E17.5 R26RLacZfl/fl Gdf5-Cre (A, C, and E) and R26RLacZfl/+ SmoM2fl/+ Gdf5-Cre (B, D, and F) mice. (B) Arrow indicates ectopic cartilage. (C–F) Insets show reduced depth of X-gal–stained cells in the cartilage (SafO-stained region) in R26RLacZfl/+ SmoM2fl/+ Gdf5-Cre mice compared with R26RLacZfl/fl Gdf5-Cre mice, as marked by the white dotted line. (G) The area of X-gal+ cells as part of the tibial plateau in the center of the joint was measured and analyzed by Student’s t test. Bars indicate mean ± SEM. *P < 0.01, n ≥ 4 per genotype. (H–Q) E17.5 Cre– and SmoM2fl/+ Gdf5-Cre hind limbs were sectioned and stained by in situ hybridization for Sox9 (H and I), Col2a1 (J and K), and Col1a1 (L and M), or by immunohistochemistry for Ki67 as a marker of proliferation (N and O). (N and O) Inset shows expression of Ki67+ cells occupying the joint space in SmoM2fl/+ Gdf5-Cre embryonic knees (O) compared with an absence of proliferating cells in Cre– mice (N). (H–O) Images are representative of n ≥ 3. Scale bars: 200 μm (A); 100 μm (C and N, insets). See also Supplemental Figure 4.