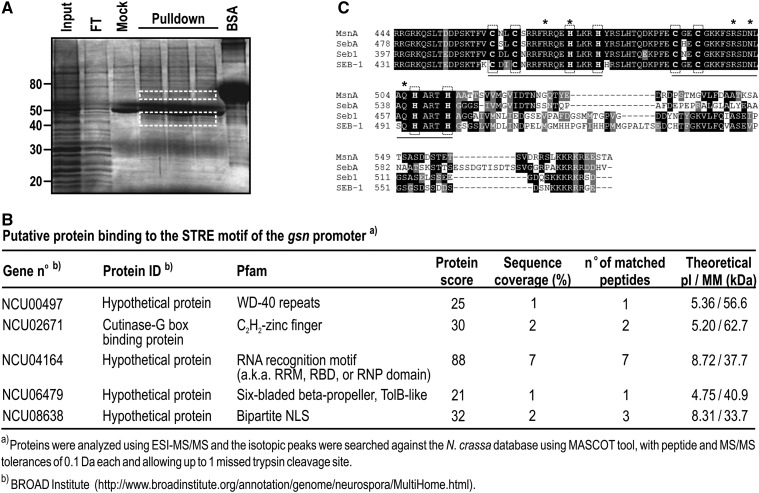
Figure 1.
Pulldown assay identified SEB-1 as the transcription factor that binds to the STRE motif in N. crassa. (A) Biotin-streptavidin pulldown assay. Biotinylated dsDNA oligonucleotides containing the N. crassa STRE consensus sequence in tandem were used as bait in a pulldown reaction with nuclear extract prepared from heat-shocked mycelia as a protein source. Protein bands not present in the mock reaction were removed from the gel, trypsin digested and submitted to mass spectrometry (white rectangles). Input: protein fraction showing DNA-binding activity; Mock: pulldown reaction without dsDNA coupled to the resin; FT: flow-through chromatographic sample. (B) The putative proteins identified by mass spectrometry. Proteins were analyzed by ESI (electrospray ionization)-MS/MS. Monoisotopic peaks were searched against the N. crassa database with a maximum of one missed trypsin cleavage and a mass tolerance of 0.1 Da for precursor ions and 0.1 Da for MS/MS spectra. Database was searched by using MASCOT. (C) Sequence alignment of different Msn2p/4p orthologs present in filamentous fungi. Alignment was done using Delta-BLAST (BLASTP 2.2.29+) in a nonredundant database. MsnA: A. nidulans ortholog (XP659256.1); SebA: A. fumigatus ortholog (XP751917.1); Seb-1: T. atroviride ortholog (AAM73769.1); SEB-1: N. crassa ortholog (EAA36208.2). The bars indicate the Zinc finger domains, and the cysteine and histidine residues are highlighted in vertical rectangles (dotted lines). The putative amino acid residues interacting with the STRE motif are indicated by asterisks. BSA, bovine serum albumin; STRE, stress response element.