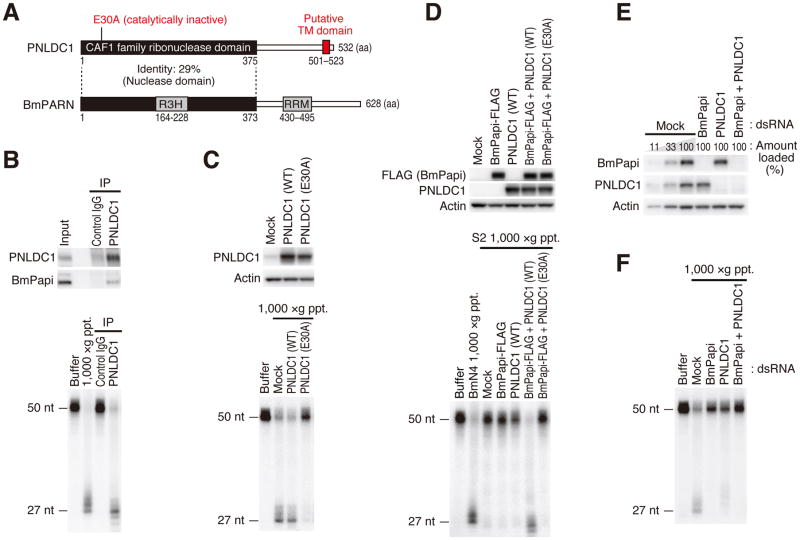
Figure 2. PNLDC1 is the silkworm Trimmer and cooperatively acts with BmPapi in trimming.
(A) Schematic representation of the domain structures of PNLDC1 (Trimmer) and PARN in silkworms. PNLDC1 has a putative transmembrane (TM) domain at the C-terminal end.
(B) PNLDC1 was immunoprecipitated from CHAPS-solubilized crude mitochondrial fraction and analyzed by Western blotting (upper panel). In vitro trimming assay was performed using the immunoprecipitated PNLDC1 complex (lower panel). PNLDC1 co-purified BmPapi and the PNLDC1 complex showed clear trimming activity.
(C) BmN4 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing wild-type or catalytically inactive (E30A) PNLDC1, and the cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting (upper panel). In vitro trimming assay was performed using 1,000 ×g pellet fraction (lower panel). While overexpression of wild-type PNLDC1 did not increase the cellular trimming activity, overexpression of E30A mutant strongly inhibited trimming.
(D) BmPapi and wild-type or catalytically inactive (E30A) PNLDC1 were expressed in Drosophila S2 cells, and the cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting (upper panel). In vitro trimming assay was performed using 1,000 ×g pellet fraction from the S2 cells (lower panel). The trimming activity was reconstituted only when BmPapi and wild-type PNLDC1 were co-expressed.
(E, F) BmN4 cells were transfected with dsRNA for BmPapi and/or PNLDC1 and the cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting (E). In vitro trimming assay was performed using 1,000 ×g pellet fraction (F). Double knockdown of BmPapi and PNLDC1 additively inhibited the trimming reaction.
See also Figure S2.