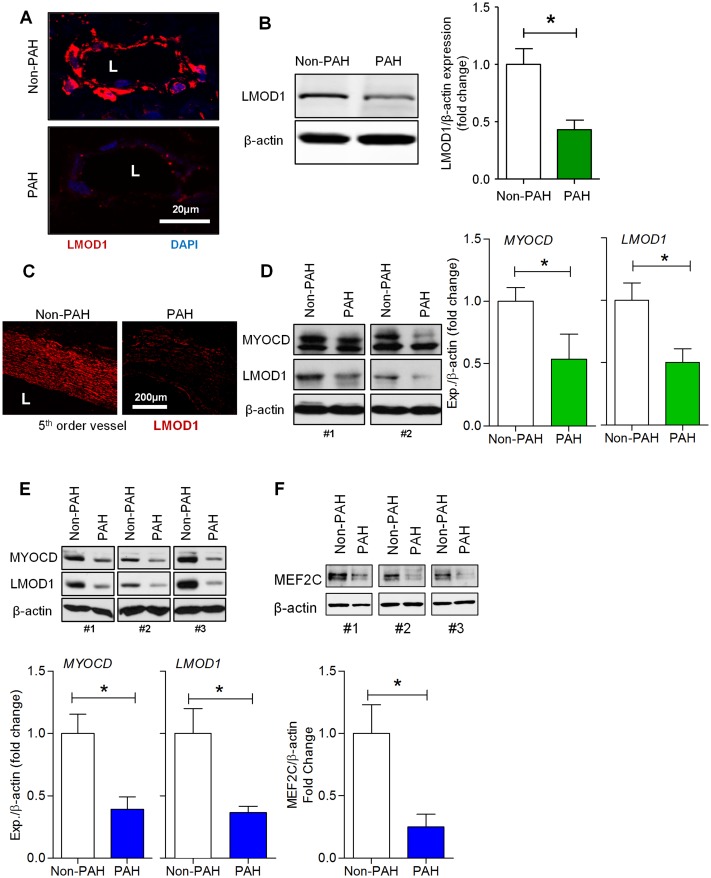
Fig 1. Contractile proteins, leiomodin1 (LMOD1), myocardin (MYOCD) and MEF2C are downregulated in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (hPASMCs) in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH).
(A,B) LMOD1 expression in lungs from PAH and non-PAH patients (n = 3) was determined by immunofluorescence and Western blot. Images from lung sections showed a marked decrease in LMOD1 expression (red fluorescence) in the vessel wall, primarily the media, of PAH samples compared to non-PAH group; DAPI nuclear staining (blue), (A). Western blot analysis of total lung homogenates showed a significant decrease in LMOD1 expression in PAH compared to control lung homogenates (B). (C-D) LMOD1 expression in the pulmonary artery (PA) from PAH and non-PAH patients (n = 3) was determined using immunofluorescence and Western blot analysis, respectively. Immunofluorescence images from PA sections of non-PAH samples showed expression of LMOD1 specific to the medial layer (smooth muscle layer, red fluorescence). LMOD1 expression was significantly attenuated in PAH samples compared to non-PAH group (C). Western blot analysis of total PA homogenates showed significant decreases in myocardin (MYOCD) and LMOD1 expression in PAH compared to non-PAH tissue homogenates (D). Western blot analysis of PASMCs-derived from PAH and non-PAH subjects showed decreased levels of MYOCD and LMOD1 protein in PAH group compared to non-PAH group (n = 3–5) (E). Western blot analysis of PASMCs-derived from PAH and non-PAH patients showed decreased levels of MEF2C protein in the PAH group compared to non-PAH subjects (n = 4) (F). Blots are representative; graphs depict mean ± SEM (*, p<0.05).