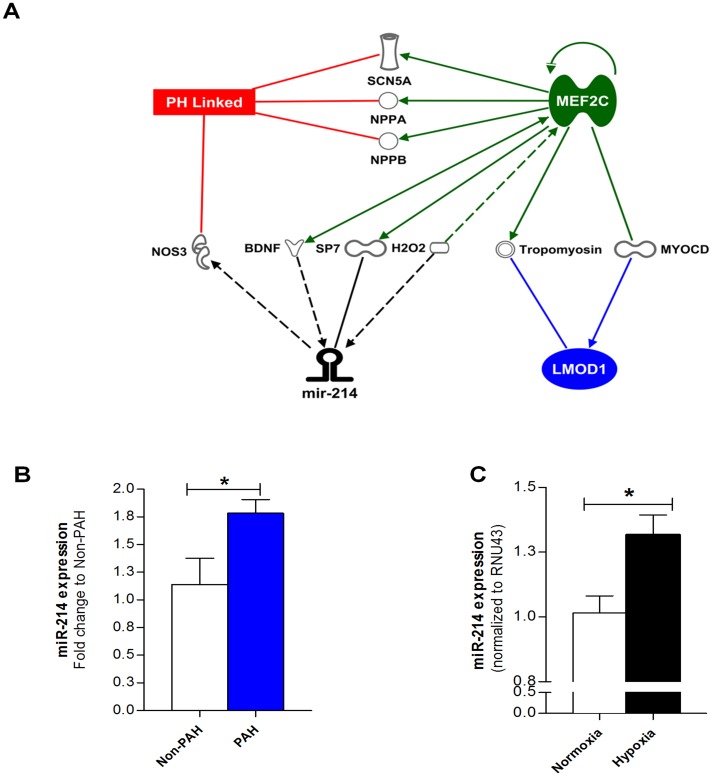
Fig 2. miR-214 is significantly upregulated in PAH.
(A) Integrated Pathway Analysis (IPA) shows potential association between miR-214-MEF2C-LMOD1 in PAH, and other genes unique to PAH potentially associated with miR-214. Relationships between molecules are represented as follows: bold line, direct interaction; dotted line, indirect interaction; line with arrowhead, represents directionality of interaction; SCN5A, sodium channel, voltage gated, type V alpha subunit; NPPA, natriuretic peptide A; NPPB, natriuretic peptide B; NOS3, nitric oxide synthase, endothelial; BDNF, brain-derived neutrotrophic factor; SP7, Sp7 transcription factor; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; MEF2C, myocyte enhancer factor 2C; MYOCD, myocardin; LMOD1, leiomodin1. (B) miR-214 expression is increased (~1.6-fold) in SMC-derived from PAH patients compared to controls subjects as measured by q-RT PCR (n = 7–8). (C) Serum-deprived control PASMCs were exposed to normoxia (21% O2) or hypoxia (1% O2) for 24 hrs and, miR-214 expression determined by q-RT PCR. Hypoxia resulted in significant increase in miR-214 expression in PASMCs compared to normoxic controls (n = 8). Graphs represent mean ± SEM. *, p<0.05 versus respective control.