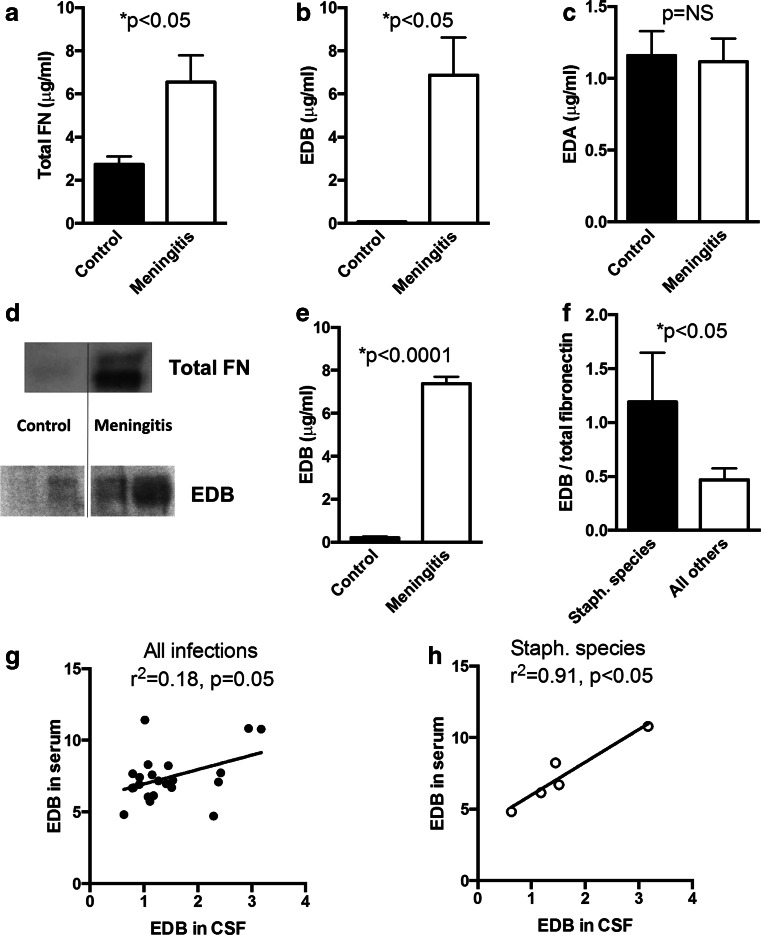
Fig. 1.
Meningitis results in elevation of EDB-containing fibronectin (EDB) in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). a Total fibronectin (total FN) is elevated in CSF of patients with bacterial meningitis 2.4-fold compared to healthy controls (n = 6 + 6). b EDB-containing fibronectin (EDB) is elevated in CSF of patients with bacterial meningitis 87-fold compared to healthy controls. c EDA-containing fibronectin (EDA) does not differ between patients with bacterial meningitis and healthy controls. CSF obtained by lumbar puncture was tested by ELISA using specific antibodies. Results represent the mean of six patients per group. d Western blot analysis confirms an increase in total fibronectin (FN) and EDB fibronectin in CSF from patients with bacterial meningitis. Protein content was measured by BCA, and the same amount of CSF was added in both wells in the top two lanes, while the same amount of total fibronectin as determined by ELISA was added in the bottom four wells (two replicates for controls and tow for meningitis are shown). FN results in two bands because it consists of a dimer. e EDB fibronectin was increased in a larger cohort of 14 controls (CT) and 22 patients with meningitis. f EDB/total fibronectin (%) is higher in patients with staphylococcus species infections (5 vs. 17). g EDB fibronectin in CSF shows a poor relationship with EDB fibronectin in serum in the whole cohort (22 patients). h In the patients with staphylococcus infections (n = 5) both correlate well