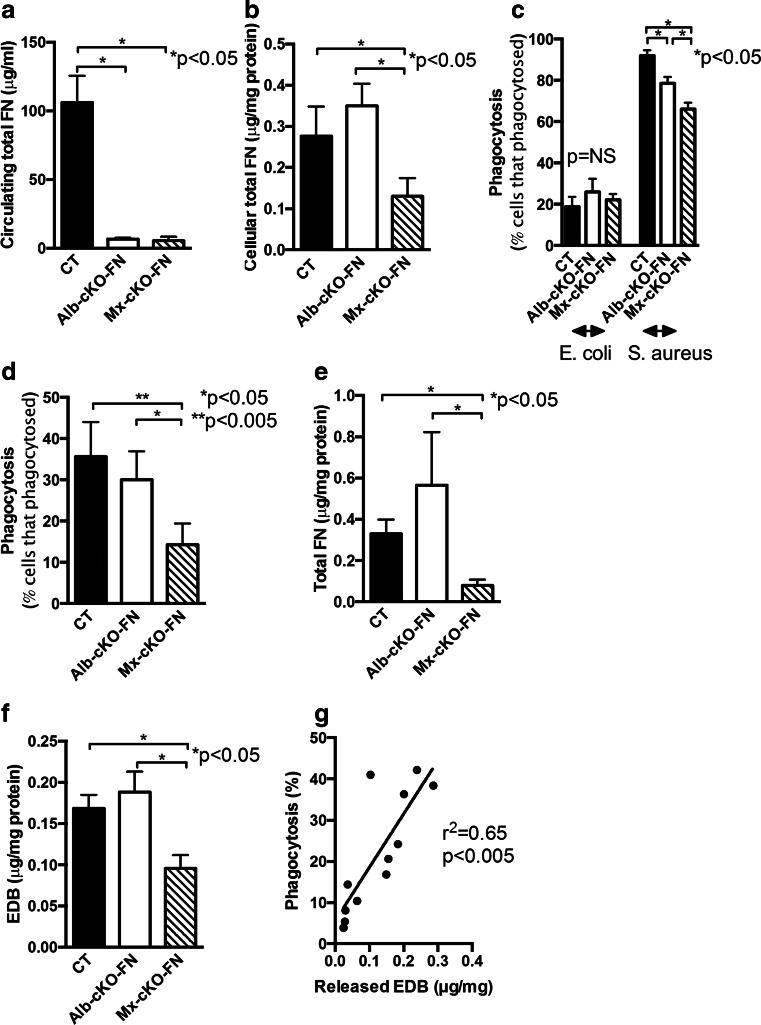
Fig. 3.
The absence of immune cell fibronectin diminishes phagocytosis. a Circulating total fibronectin (FN) is diminished when fibronectin is deleted in the hepatocytes (Alb-cKO-FN) to a similar degree as the decrease when fibronectin is deleted in the hepatocytes and in the immune cells (Mx-cKO-FN). Blood obtained from the tail vein was examined by ELISA. N = 7–10 mice per group. b Cell lysates show a decrease in total fibronectin and in EDB fibronectin in Mx-cKO-FN mice, but not in Alb-cKO-FN mice as determined by ELISA of the cell lysates and correcting to total protein measured by BCA. N = 5/group. c In a phagocytosis test (Phagotest) where bacteria are added to total blood and phagocytosis is determined after 10 min, deletion of circulating fibronectin diminished phagocytosis of S. aureus (Alb-cKO-FN), but this decrease was more pronounced when both circulating and immune cell fibronectin were deleted (Mx-cKO-FN). Phagocytosis of E. coli was not affected by fibronectin availability. d In a phagocytosis test in which the cells are separated from the serum and the bacteria opsonized with control serum, phagocytosis with cells from Alb-cKO-FN is similar to CT. Deletion of fibronectin in the immune cells in Mx-cKO-FN results in a significant decrease in phagocytosis. N = 5 pools of blood from 3–5 mice/pooled group. e–f The decrease in phagocytosis is associated with a decrease in total (e) and EDB fibronectin (f) released in the media and corrected to protein. N as in D. g The levels of EDB fibronectin released in the media correlates with the degree of phagocytosis in CT mice. N = 12 pools of blood from 2–3 mice/pooled group