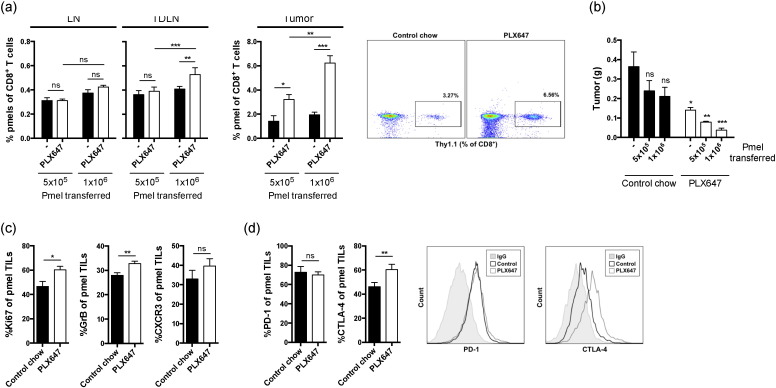
Fig. 3.
CSF-1R blockade increases antigen-specific T cell activity at the tumor site. (a) Mice were injected with B16-IDO tumor cells and treated with PLX647 or control chow. Five days after tumor challenge mice adoptively received in vitro activated pmel CD8+ T cells and were sacrificed 2 weeks after tumor challenge. Average percentage and representative dot plots of pmel cells of total CD8+ T cells in LN, TDLN, and tumors in each group of mice are shown. (b) B16-IDO tumor size in mice after adoptive transfer of increasing numbers of CD8+ pmel T cells and treatment with PLX647 or control chow. (c) Expression of CXCR3, Ki-67 and Granzyme B on tumor-infiltrating CD8+ pmel T cells isolated from mice treated with PLX647 or control chow. (d) Percentage tumor-infiltrating CD8+ pmel T cells from mice treated with PLX647 or control chow expressing PD-1 and CTLA-4 and representative flow histograms. Data are shown as mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments.