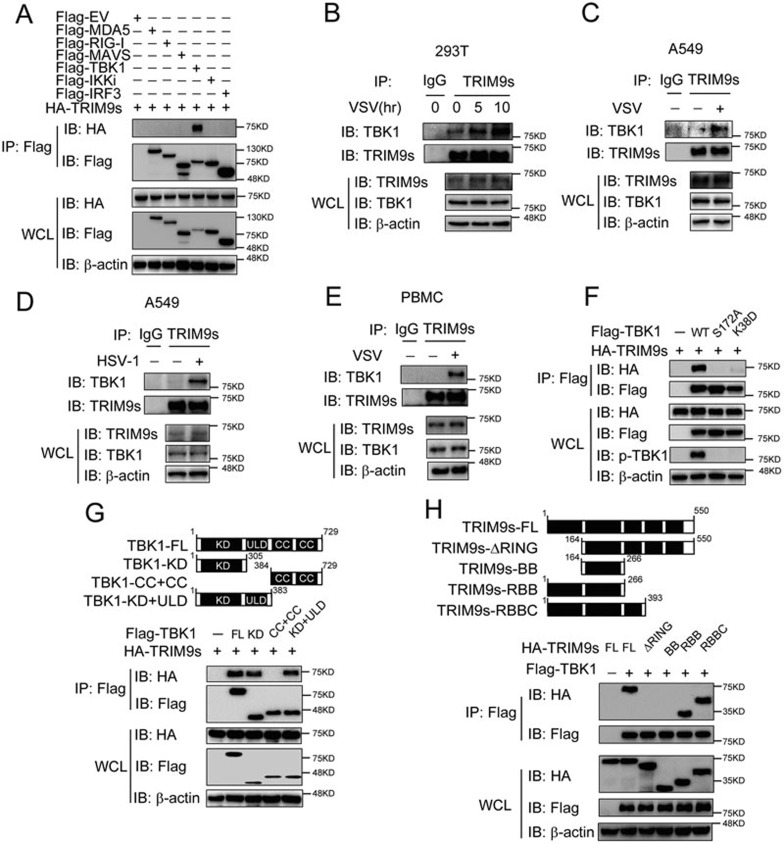
Figure 3.
TRIM9s interacts with TBK1 upon viral infection. (A) Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) and IB analysis of 293T cells transfected with various combinations (above lanes) of plasmids for Flag-MDA5, Flag-RIG-I, Flag-MAVS, Flag-TBK1, Flag-IKKi, Flag-IRF3, and HA-TRIM9s. (B-E) 293T cells (B), A549 cells (C, D) or PBMCs (E) were infected with VSV (B, C, E) or HSV-1 (D) and collected at the indicated time points. Cell extracts were harvested for IP with anti-TRIM9s, followed by IB analysis with anti-TBK1 antibody. (F) 293T cells were transfected with HA-TRIM9s and Flag-TBK1 or various mutants. Whole cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag beads, followed by IB analysis with anti-HA antibody. (G) Co-IP and IB analysis (bottom) of 293T cells transfected with TBK1 deletion mutants (top) along with HA-TRIM9s. WT, wild-type; KD, kinase domain; ULD, ubiquitin-like domain; CC, coiled-coil domain. (H) 293T cells were transfected with Flag-TBK1 and the deletion mutants of TRIM9s (top). Whole-cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag beads, followed by IB analysis with anti-HA antibody. Data are representative of three independent experiments with similar results.