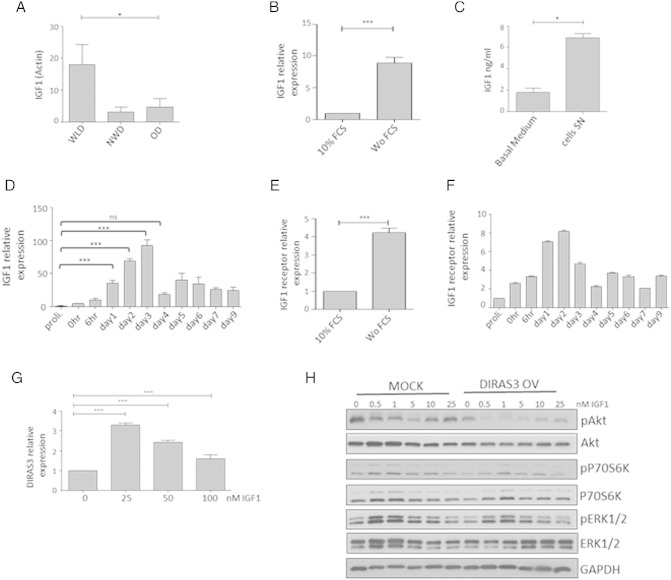
Fig. 6.
Long-term WL induces IGF-1 expression in human ASCs. IGF-1 is up-regulated during adipogenesis and IGF-1-induced Akt–mTOR activation is counteracted by DIRAS3. (A) IGF-1 expression was studied by q-RT-PCR in ASCs derived from WLDs (n = 4), NWDs (n = 3) and ODs (n = 3) normalized to actin. (B) IGF-1 expression was analyzed upon serum starvation of ASCs in reference to actin gene. (C) IGF-1 concentration in supernatant (SN) of ASCs derived from sWAT of WLDs after 3 days of cultivation in basal medium (containing 10% FCS) relative to basal medium (containing 10% FCS) was determined by human IGF-1 ELISA kit (Ref: E20, Lot: 120115, Mediagnost, Germany). (D) IGF-1 expression was investigated in the course of adipogenesis using q-RT-PCR normalized to actin. (E) IGF-1-R expression was analyzed upon serum starvation of ASCs using actin as reference gene. (F) IGF-1R expression normalized to actin was investigated in the course of adipogenesis using q-RT-PCR. (G) DIRAS3 expression in ASCs at 6 h after addition of IGF-1 was quantified by q-RT PCR employing actin as reference gene. (H) ASCs were infected with mock or DIRAS3 overexpression lentiviruses. Cells were starved for 48 h followed by addition of increasing concentrations of IGF-1 for 10 min. Phosphorylation of Akt (S473), S6K1 (T389) and ERK1/2 (T282/Y204) was examined by Western blotting. All error bars represent the means ± SEM. p values * = p < 0.05, ** = p < 0.001 and *** = p < .0001 (number of donors = 3). The significance of difference between means was assessed by analysis of variance (ANOVA) (A, D and G) and Student's t test (B, C and E).