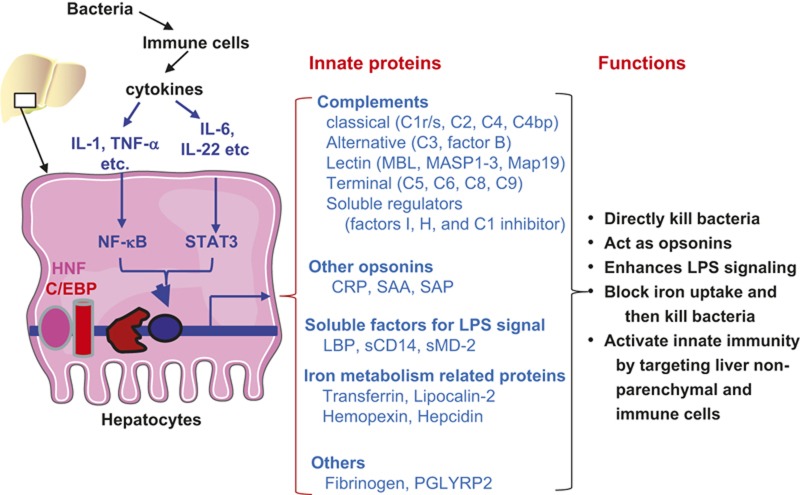
Figure 1.
Critical roles of hepatocytes in anti-bacterial innate immunity. Upon bacterial infection, immune cells secrete cytokines to stimulate hepatocytes to produce anti-bacterial proteins. The pro-inflammatory cytokines activate the transcription factors NF-κB and STAT3. Along with liver-enriched transcription factors HNFs and C/EBPs, they promote the expression of many anti-bacterial proteins as listed. These proteins eliminate the bacteria and orchestrate the innate immune function.