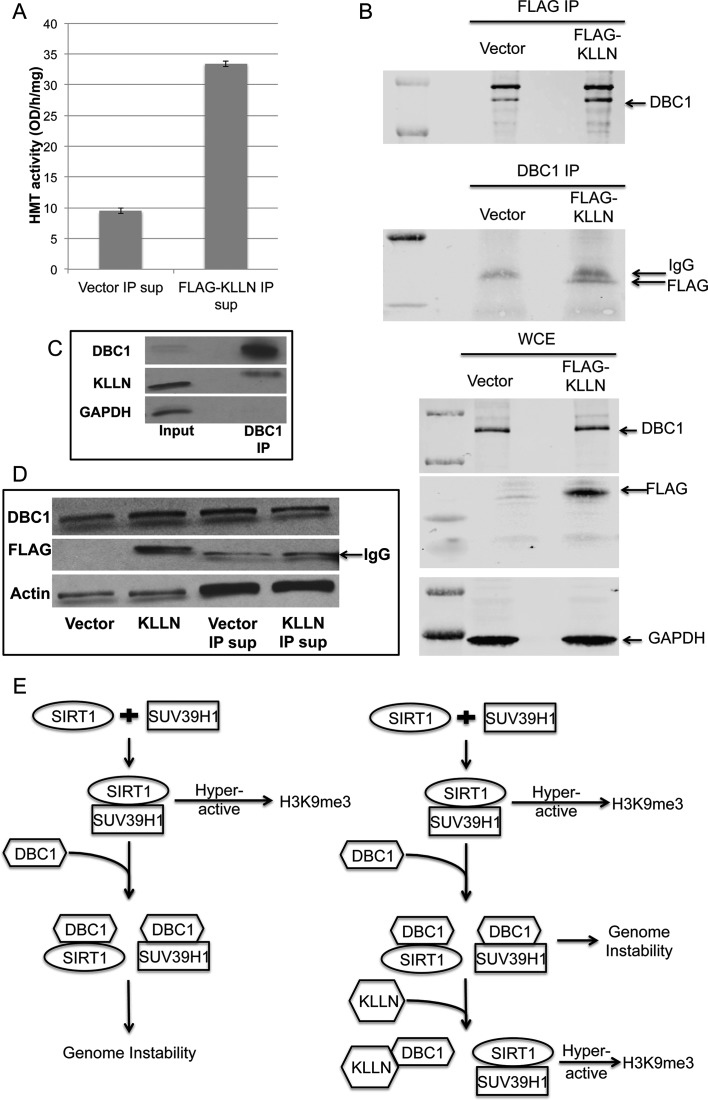
Figure 4.
KLLN interaction with DBC1. (A) Graph of H3K9-specific methyltransferase activity using supernatant of nuclear fraction after IP with FLAG antibody in MCF7 cells transfected with FLAG-KLLN or vector alone. H3K9 methyltransferase activity was increased in supernatant without KLLN or its interacting proteins. (B) Immunoblot analysis of co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) with FLAG or DBC1 antibody. KLLN and DBC1 shown to interact with each other. (C) Immunoblot analysis of lysates immunoprecipitated using DBC1 antibody in untreated MCF7 cells. Endogenous KLLN was successfully pulled down by DBC1 antibody. (D) Immunoblot analysis of nuclear fraction lysates from FLAG-KLLN transfected MCF7 cells and supernatant lysate after IP with FLAG antibody to pull down KLLN and its interacting partners. The supernatant after IP had reduced DBC1 protein levels. (E) Schematic of mechanism for KLLN regulation of H3K9me3 (modified from Li et al., 2009). KLLN interaction with DBC1 abrogates DBC1 inhibition of SUV39H1, an H3K9 trimethylation-specific histone methyltransferase.