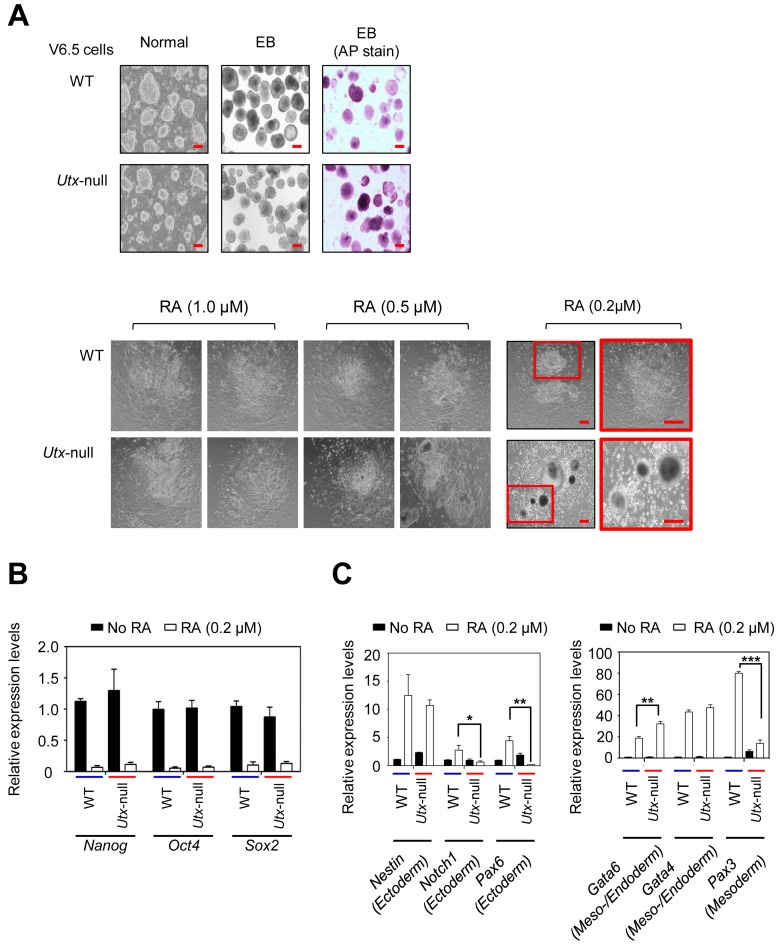
Figure 1.
UTX loss impedes RA-driven mouse ESC differentiation (A) Microscopy images of WT and Utx-null V6.5 mouse ESCs during RA-induced differentiation. WT or Utx-null cells were plated on petri dishes and cultured to form EBs by withdrawing LIF for 5 days. EBs were treated with all-trans RA (0.2 μM, 0.5 μM or 1 μM) to induce differentiation for 5 days. AP, alkaline phosphatase; Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis showed that UTX loss had no significant effect on the RA-induced reduction of Nanog, Oct4 and Sox2 mRNA levels. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis showed that UTX loss had a negative effect on the RA-induced increases of Notch1, Pax6 and Pax3 mRNA levels. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (error bars) of at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 indicate statistically significant changes.