Figure 6.
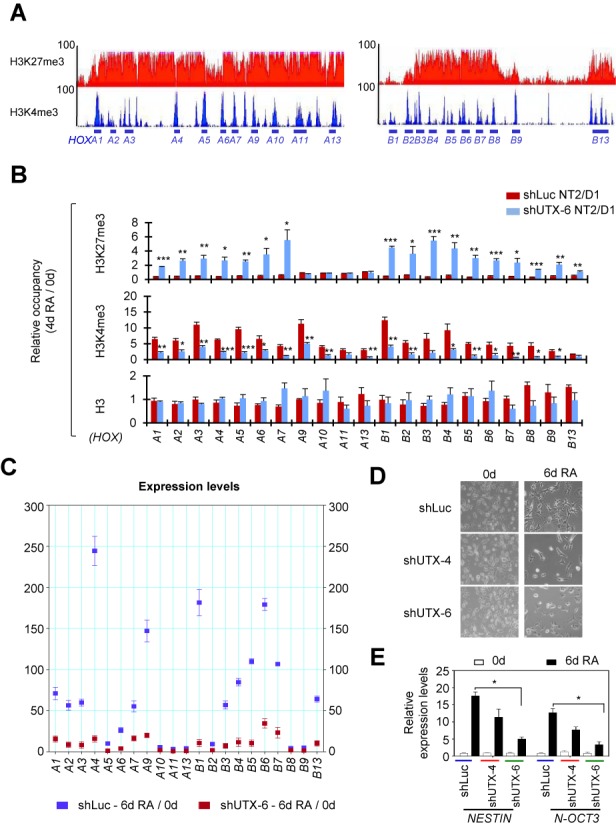
During RA-driven differentiation of human NT2/D1 cells, UTX is responsible for the bivalency resolution and activation of most RA-inducible bivalent HOXA and HOXB genes. (A) ChIP-Seq density profiles of H3K27me3 (red) and H3K4me3 (blue) at the human HOXA and HOXB cluster genes in NT2/D1 cells. The vertical axis shows the coverage for histone methylation set at a maximal value of 100. (B) Effect of UTX knockdown on the RA-induced changes in H3K27me3, H3K4me3 and H3 levels at the HOXA and HOXB cluster promoters in NT2/D1 cells. shLuc- or shUTX-6-treated cells were cultured in media containing 10 μM RA for 0 or 4 days. Chromatin levels for histone marks were analyzed using a quantitative ChIP assay. PCR values for each time point were normalized to input. The relative occupancy represents the fold change in chromatin levels from day 0 to day 4 (4d/0d). (C) Effect of UTX knockdown on the RA-induced changes in the expression levels of HOXA and HOXB cluster genes. shLuc- or shUTX-6-treated NT2/D1 cells were incubated with 10 μM RA for 0 or 6 days. mRNA levels were analyzed using quantitative RT-PCR. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (error bars) of least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 indicate statistically significant changes. (D and E) Effect of UTX knockdown on morphological changes (D) and activation of NESTIN and N-OCT3 gene (E) during the RA-induced differentiation of NT2/D1 cells. UTX was depleted using shUTX-4 and shUTX-6 in NT2/D1 cells. Cells (2–5 × 104) were seeded and treated with 10 μM RA for 0 or 6 days. Cell differentiation patterns were monitored using a microscope. Representative microscopy images of three independent experiments are shown (magnification 40X). Expression levels of NESTIN and N-OCT3 gene were measured by quantitative RT-PCR.
