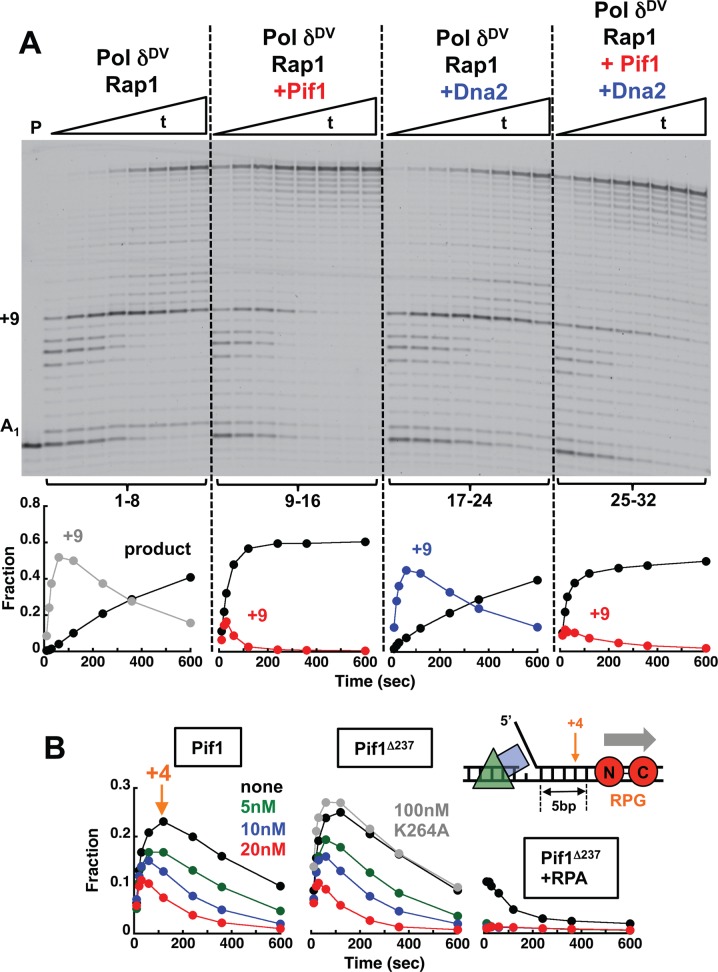
Figure 4.
Pif1 allows Pol δ to bypass a Rap1 block. (A) Primer extension assays with PCNA-loaded Pol δDV (25 nM) using the DNA (25 nM) in Figure 1A bound to Rap1 (100 nM). The experiments were performed in the absence (lanes 1–8) or presence of 20 nM Pif1 (lanes 9–16), 20 nM Dna2 (lanes 17–24) or 20 nM Pif1 and 20 nM Dna2 (lanes 25–32). The graphs show quantitation of the full-product and the +9 position in the downstream duplex. (B) Quantitation of full-product and the +4 position using the indicated DNA (25 nM) bound to Rap1 (100 nM). The primer extension assays were performed with PCNA-loaded Pol δDV (25 nM) in the absence (black) or presence of 20 nM (red), 10 nM (blue) or 5 nM (green) of either Pif1 (left) or its variant missing the first 237 amino acids and its ATPase inactive form (middle). The experiments in the right panel were performed in the presence of 50 nM RPA.