Figure 5.
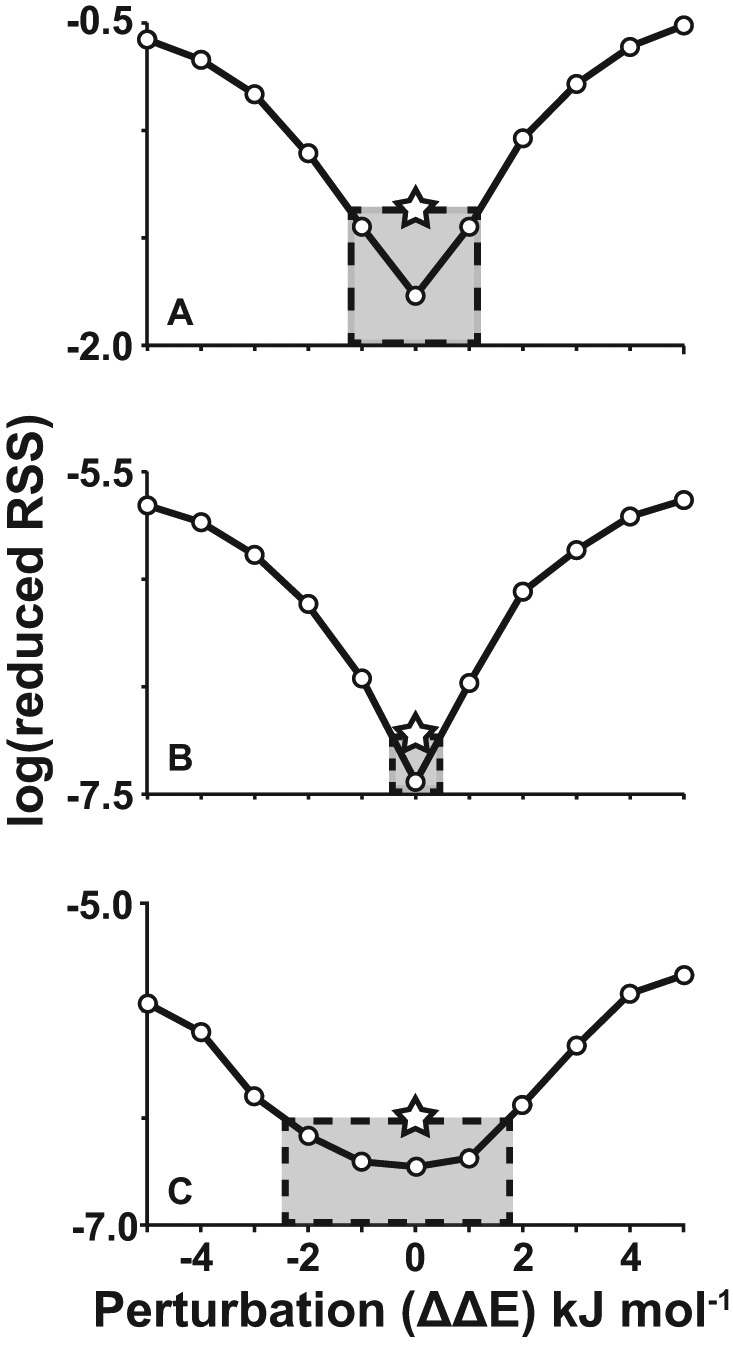
Sensitivity of the global fit to thermodynamic perturbations. Increasing thermodynamic mismatch between trapped mutants and their corresponding GR isomers (ΔΔE) leads to larger values of ‘reduced RSS’ in global fits, i.e. poorer overall agreement. The reduced residual-sum-of-squares (RSS) is the residual-sum-of-squared differences between the simulated data points and the best global fit to the simulated data points, divided by the degrees of freedom of the fit (#simulated data points – #adjusted parameters). Simulations are shown for c-myc Pu18 GQ (A) DSC and (B) UV-Vis data, and (C) PIM1 UV-Vis data using dG>dI mutations (See Supplementary Figures S5 and S6 for dG>dT simulations). Simulated data sets (1000 and 25 iterations for c-myc and PIM1 data sets, respectively) were prepared in which the folding ΔH and T0ΔS values of the trapped mutants differed from those of the corresponding wild-type GR isomers by random perturbations with a mean of zero and standard deviation of ΔΔE kJ mol−1. Simulated data sets were analyzed according to the global fitting method (Equations 1–14). Larger thermodynamic perturbations led to poorer fits, as indicated by larger RSS fitting residuals (Equation 14). The stars correspond to the ‘reduced RSS’ values obtained for the true experimental data sets. These define the maximum average mismatch between the folding thermodynamics of trapped mutants and corresponding wild-type GR isomers (gray shaded boxes). For thermodynamic perturbations larger than 1.1–1.5 kJ mol−1 (DSC) or 0.2–0.5 kJ mol−1 (UV-Vis), the RSS is greater than what we observe experimentally. In other words, the root-mean-squared (RMS) difference between the folding parameters of the trapped mutants and the corresponding wild-type GR isomers is not much more than this tolerance. For points of reference, the ceiling for perturbations is about 0.5% of the total folding enthalpies (ΔHF) of the GQs and 3% of the ΔΔHF between the most and least stable trapped mutants.
