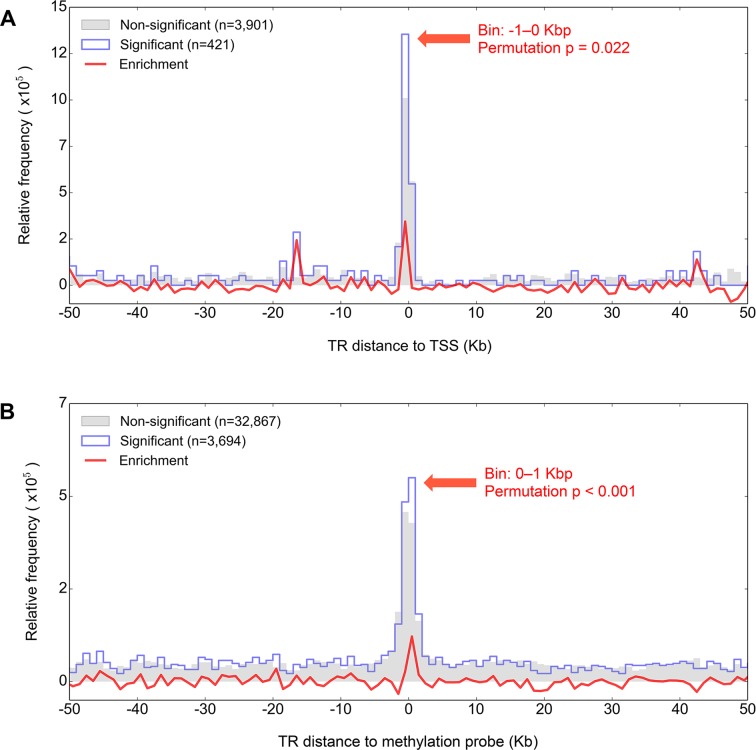
Figure 5.
TRs that are significant eQTLs and mQTLs preferentially co-localize with their associated target. After first dividing eQTL and mQTLs into those that were either nominally significant (P < 0.05 in either CEU or YRI, blue outline) or non-significant (P > 0.05 in both CEU and YRI, gray shading), we plotted the separation of (A) TR:TSS and (B) TR:CpG pairs for the two groups in 1 kb bins. The red line shows the frequency difference between the non-significant and significant distributions, with the significance of the enrichment determined through permutations (see ‘Materials and Methods’ section). For both eQTLs and mQTLs, significant associations are enriched for separations of <1 kb. These results mirror those from previous studies using SNPs, which have shown a strong enrichment for eQTLs occurring in close proximity to the TSS of the associated gene (43), and for mQTLs to colocalize with their associated CpG (44).