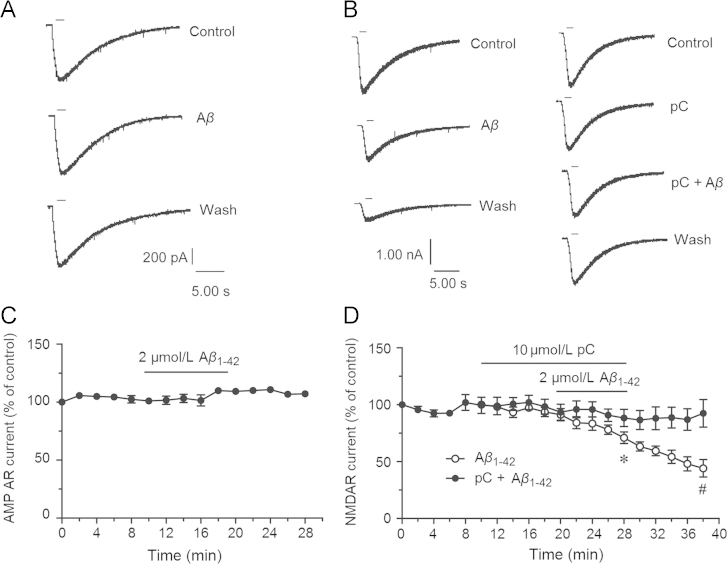
Figure 6.
Parishin C protected against inhibition of NMDAR currents by 2 μmol/L soluble Aβ1–42 oligomers but not AMPAR currents in primary cultured hippocampal neurons. Holding potential was –70 mV and external solution was with 0.1 μmol/L TTX, and without Mg2+. (A) Bath perfusion of 2 μmol/L soluble Aβ1–42 oligomers for 10 min had no effects on AMPAR currents. Short bar means pressure injection of 3 μmol/L AMPA. (B) Bath perfusion of 2 μmol/L soluble Aβ1–42 oligomers for 10 min inhibited NMDAR currents, and the inhibition continued during wash. Parishin C (10 μmol/L) perfusion 10 min beforehand prevented Aβ’s inhibitory effects. Short bar meant pressure injection of 100 μmol/L NMDA and 10 μmol/L glycine. (C) The AMPAR currents were not changed during soluble Aβ1–42 oligomers perfusion (n=3). (D) Soluble Aβ1–42 oligomers significantly inhibited NMDAR currents but it was rescued by perfusion of parishin C (Aβ1–42 group n=5, pC+ Aβ1–42 group n=6). ⁎P<0.05 vs. currents before perfusion, #P<0.05 vs. Aβ1–42 group. Data are mean±SEM. The amplitudes of all currents were normalized to the first evoked at –70 mV.