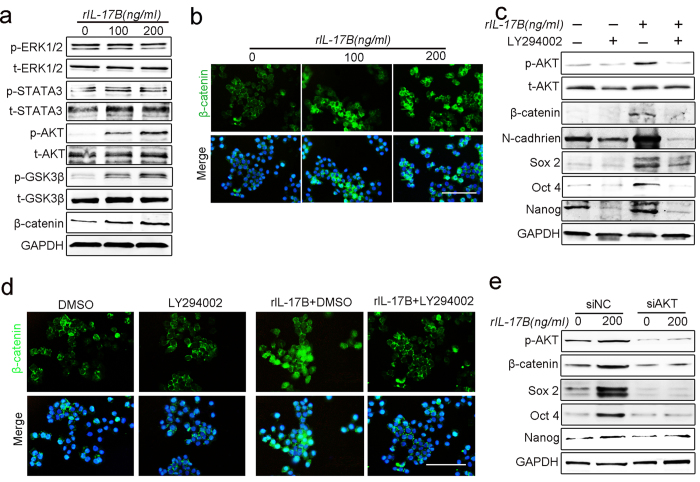
Figure 6. IL-17B activates the AKT/β-catenin pathway in a concentration-dependent manner.
(a) The expressions of total and phosphorylated ERK1/2, AKT, STAT3, GSK-3β, and β-catenin were determined by western blot analyses of MGC-803 cells treated with corresponding concentrations of rIL-17B for 48 h, the blots were cropped from different gels but all the gels had been run under the same experimental conditions. (b) The nuclear translocation of β-catenin was detected by immunofluorescence in MGC-803 cells treated with corresponding concentrations of rIL-17B for 48 h, scale bar = 100 μm. (c) Western blot analysis for p-AKT and total AKT, β-catenin, N-cadherin, Sox2, Oct4, and Nanog in MGC-803 cells treated with rIL-17B (200 ng/mL) for 48 h in the presence or absence of 50 μM/mL of LY294002, the blots were cropped from different gels but all the gels had been run under the same experimental conditions. (d) MGC-803 cells were treated with rIL-17B (200 ng/mL) for 48 h in the presence or absence of LY294002 (50 μM/mL). The nuclear translocation of β-catenin was detected by immunofluorescence. Scale bar = 100 μm. (e) MGC-803cells were transfected with AKT siRNA or the matching scramble control siRNA, then western blot analysis for p-AKT, β-catenin, Sox2, Oct4, and Nanog in MGC-803 cells treated with rIL-17B (200 ng/mL) for 48 h, the blots were cropped from different gels but all the gels had been run under the same experimental conditions.