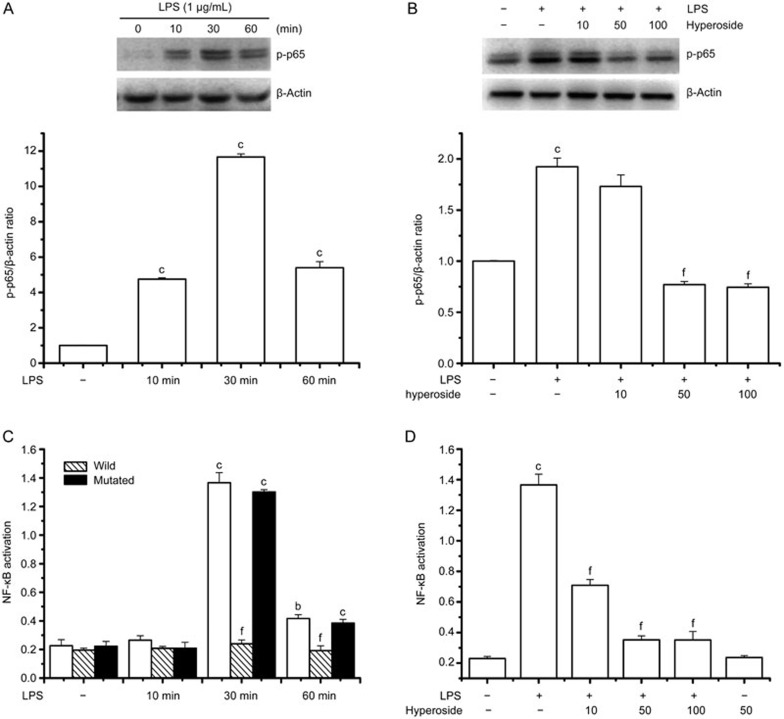
Figure 5.
Effect of hyperoside on LPS-induced phosphorylation of p65 and DNA binding activity of NF-κB. RA FLSs were incubated with LPS (1 μg/mL) for the indicated time with or without the indicated concentration of hyperoside. In coincubation experiments, hyperoside was added to cells 4 h prior to LPS and then treated with LPS for 30 min. The nuclear extracts of these cells were prepared for Western blotting and measurement of NF-κB DNA binding activity. (A and B) Representative immunoblot comparing phosphorylated p65 to β-actin in RA FLSs after the indicated treatment. Group data showing the normalization of phosphorylated p65 to β-actin as determined in each group from the 3 independent experiments. (C and D) Nuclear extracts prepared from cells exposed to LPS for 30 min exhibited increased NF-κB DNA binding activity, which was significantly prevented by hyperoside. The NF-κB DNA binding capacity was effectively completed by the wild-type consensus oligonucleotide, but not mutated oligonucleotide. Values are the mean±SEM of the three independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with the untreated control. ##P<0.01 compared with the LPS-treated group.