Figure 1.
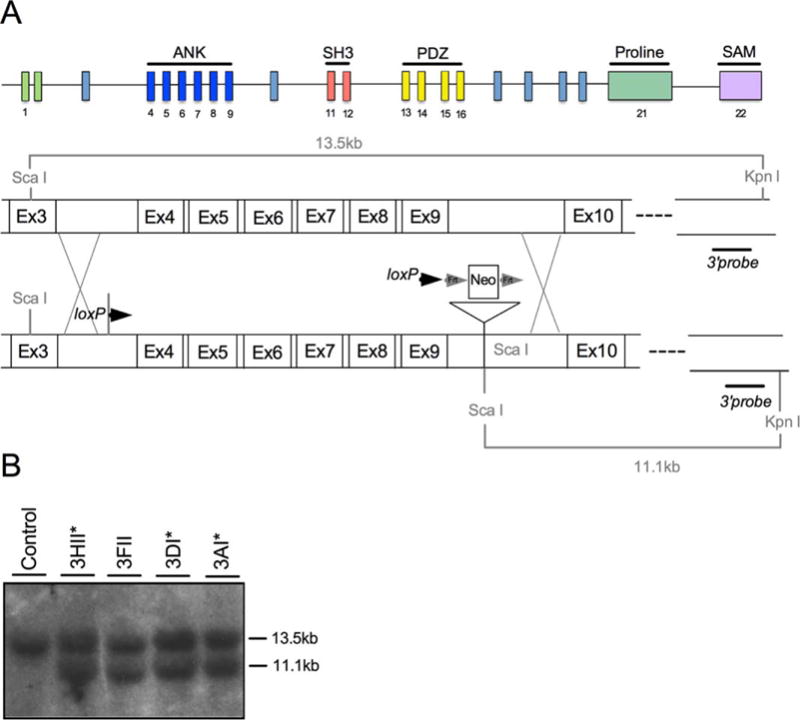
Genetic deletion of Shank3 exons 4–9. (A) Schematic of the Shank3 gene displaying exons and their respective domains (ANK—Ankyrin repeat domain; SH3—Src Homology 3 domain; PDZ—PSD95/Dlg1/Zo1 domain; SAM—Sterile alpha motif) (top). Schematic of the targeted portion exons 4–9 of Shank3 (middle) and the insertion of the targeting construct following recombination (bottom). (B) Southern blot of ScaI and KpnI-digested DNA from control (lane 1) and neo-resistant ES cells (lanes 2–5) reveals 13.5 kb and 11.1 kb ScaI and KpnI fragments reflecting proper targeting in clones that were selected for blastocyst injections (asterisks).
