Figure 3.2.
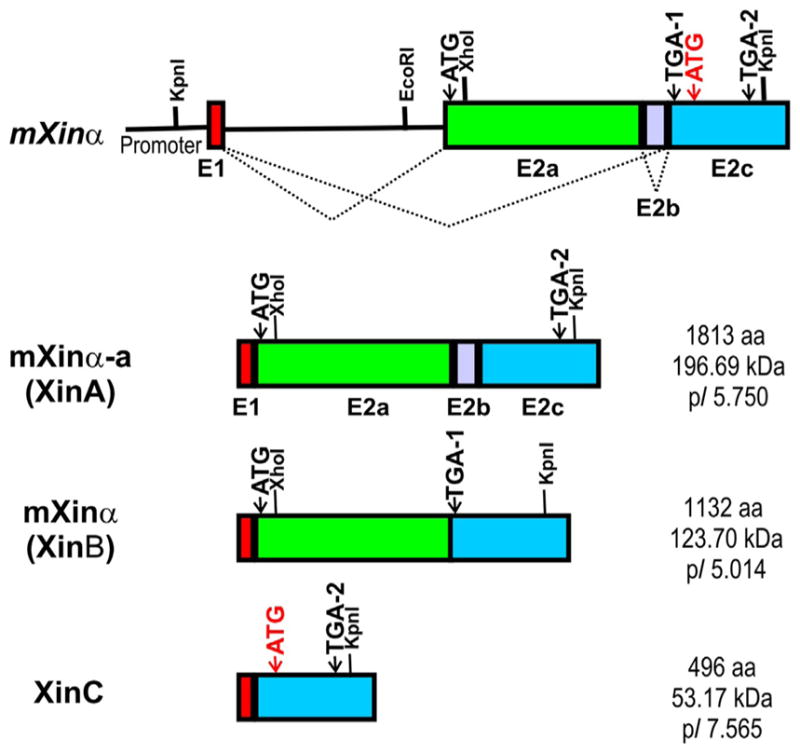
Schematic diagrams of mouse Xirp1/mXinα genomic organization and its encoded message and protein variants. The mouse Xinα gene contains a small exon E1 and a large exon E2. After removal of intron between E1 and E2, the E2 can further undergo an unusual intra-exonic splicing to give rise to two message or protein variants containing either whole E2 (mXinα-a or XinA) or E2 without E2b (mXinα or XinB) (Gustafson-Wagner et al., 2007; Otten et al., 2010). The predicted amino acid number, molecular mass, and pI value for each mouse Xinα protein variants are listed to the right of their respective message diagrams. Similar gene organization and splicing events including the intra-exonic splicing were also found in human XIRP1/hXinα gene (van der Ven et al., 2006). Another splicing event to remove E2a and E2b leading to a smallest message (XinC) has been detected by RT-PCR from normal mouse or human hearts. However, Western blot analysis with specific antibody barely detected the XinC protein from hypertrophic human hearts but not from normal mouse or human hearts (Otten et al., 2010). The predicted XinC protein has a relatively higher pI value and its sequence is identical to the C-terminus of mXinα-a/XinA. It is difficult to rule out that the detected XinC from hypertrophic human hearts may represent degraded product of XinA.
