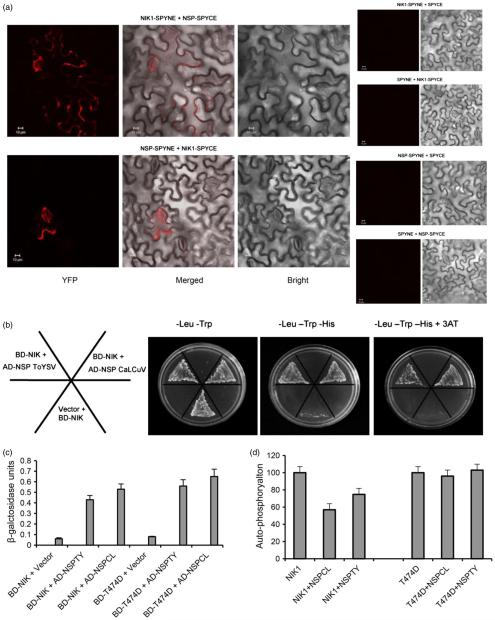
Figure 1.
T474D, a hyperactive AtNIK1 mutant, bypasses NSP inhibition and yet binds to ToYSV NSP. (a) In vivo interaction between NSP from CaLCuV and AtNIK1 by BiFC analysis. Fluorescence (YFP), bright and merged confocal images were taken of epidermal cells of tobacco leaves co-expressing NIK1-YFPC (NIK1-SPYCE) +NSP-YFPN (NSP-SPYNE) or NIK1YFPN (NIK1-SPYNE) + NSP-YFPC (NSP-SPYCE) fusion proteins in the presence of HC-Pro suppressor, 2 h after agro-infiltration with the indicated DNA constructs. Negative controls are shown on the right. Scale bars = 10 μm. (b) and (c) Interactions of ToYSV NSP with AtNIK1 and T474D. NSPs from CaLCuV (NSPCL, control) and ToYSV (NSPTY) were expressed in yeast as GAL4 activation domain (AD) fusions (AD-NSP ToYSV and AD-NSP CaLCuV), and the kinase domains of AtNIK1 (NIK) and T474D were expressed as GAL4 binding domain (BD) fusions (BD-NIK). Interactions between the tested proteins were examined by monitoring His prototrophy (b) and confirmed by measuring the activity (mean ± SD, n = 3) of the β-galactosidase reporter enzyme corresponding to the second reporter gene β-Gal (c). Error bars represent the confidence interval (α = 0.05) of three technical replicates. (d) ToYSV NSP inhibits AtNIK1 autophosphorylation, but does not suppress T474D kinase activity. The kinase domain of AtNIK1 (NIK1) or T474D was expressed as a GST fusion and incubated with [γ-32P]ATP in the presence or absence of GST-NSP. Phosphorylated proteins were quantified by counting the scintillation of the excised protein bands. Autophosphorylation activity in the presence of NSP was expressed as the percentage of the total activity of NIK1 or T474D alone. Error bars represent the confidence interval (α = 0.05) of three technical replicates from two independent experiments.