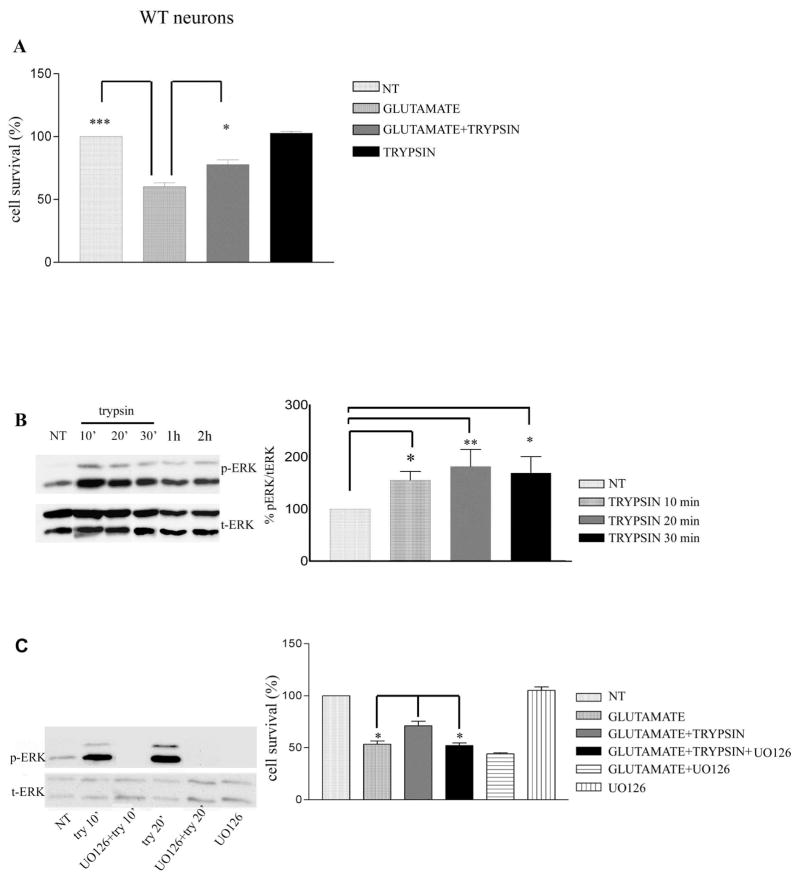
Figure 1. Trypsin induces neuroprotection via ERK1/2 phosphorylation.
(A) WT mouse cortical neurons at 7 days in vitro (DIV) were pretreated with 5.25 nM trypsin for 60 minutes followed by incubation with 50 μM glutamate for 3 hours. Cells were then fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and stained with Hoechst 33342 as described (20). Nine pictures were taken from each well and each condition represented the average of 3–4 wells. Cell survival was measured by counting the number of cells with normal nuclear morphology (wt vs glutamate, P<0.001, glutamate vs glutamate+trypsin P<0.05, glutamate+trypsin vs glutamate+trypsin+UO126 P=0.05). Results (mean ± standard error [SE]) were calculated from 4 independent experiments. * p<0.05, ** p <0.005, *** p<0.001 comparing cultures treated with glutamate in the presence or absence of trypsin (One-way Anova, Tukey’s post-hoc). (B) Mouse cortical neurons were cultured and treated with trypsin as above for the indicated time periods. Untreated cultures were used as controls (NT). Following incubation, cells were collected and assayed on Western blots (WBs) for the indicated proteins. (Left) A representative blot out of 7 independent experiments is shown. (Right) Densitometric analysis of p-ERK 1/2 in the presence of trypsin at different time points expressed as percentage of phospho-ERK 1/2 (p-ERK) to total ERK 1/2 (t-ERK) ratio that was set as 100% for control (NT). Bars represent phospho-protein to protein ratios relative to control. (C) ERK 1/2 inhibitor U0126 (10 μM) blocked trypsin-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Inhibitor was added to cultures 30 minutes prior to addition of 5.25 nM trypsin. Neurons were subsequently collected at the indicated times and subjected to SDS-PAGE and WBs as above (Left). (Right) Quantitative data show that UO126 inhibits trypsin-induced neuroprotection against glutamate. Results (mean ± standard error [SE]) were calculated from 4 independent experiments. *p<0.05, ** p <0.005 (Tukey’s post-hoc). UO126 shows no toxicity when administered in culture.