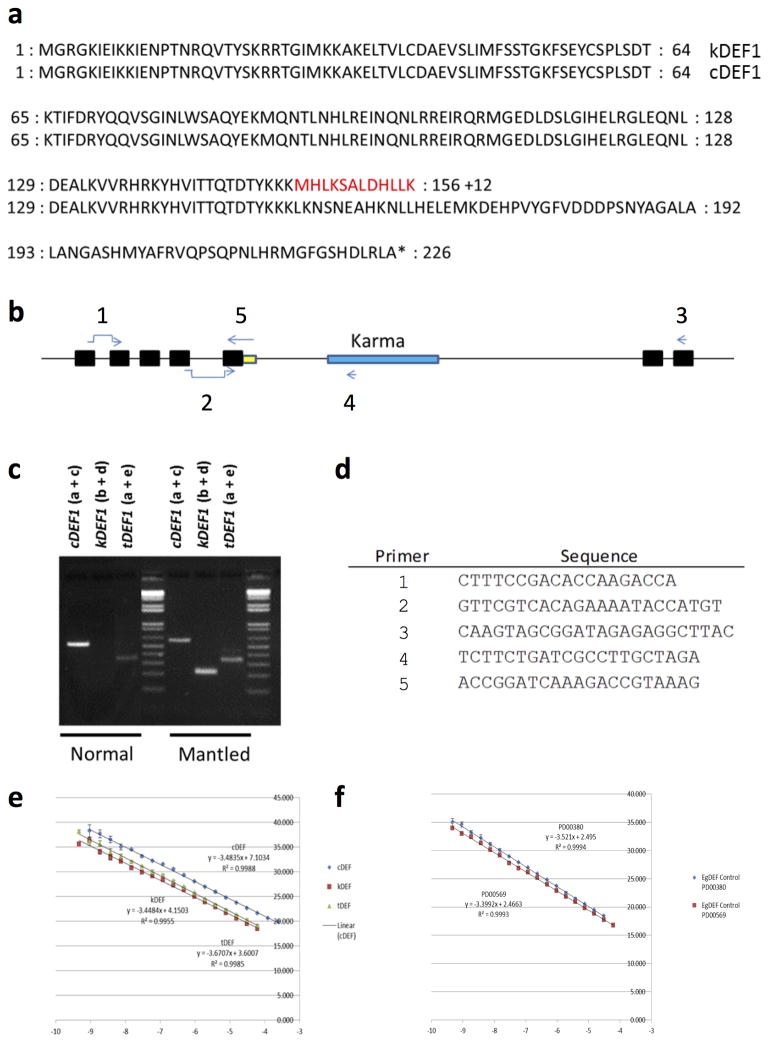
Extended Data Figure 7. Protein sequences and summary of qRT-PCR assay designs.
a, Residues highlighted in red are encoded by Karma sequence splice to exon 5 of EgDEF1. The alternate splicing event disrupts the transcription activation domain of EgDEF1. 12 variant amino acids are coded by Karma sequencing, followed by a stop codon. b, Diagram of EgDEF1 locus including positions of qRT-PCR primers. cDEF1 transcripts were detected using primer a (spanning the splice junction of exons 1 and 2) and primer c (internal to exon 7). kDEF1 transcripts were detected using primer b (spanning the splice junction of exons 4 and 5) and primer d (internal to Karma ORF2). tDEF1 transcripts were detected using primer a and primer e (spanning the 3′ end of exon 5 and including tDEF1-specific intron 5 sequence. c, All assays were confirmed to give a single band of the correct size by agarose gel electrophoresis. Amplicons were Sanger sequence verified. Note that no band is amplified using the kDEF1 primer pair in samples from normal inflorescence, consistent with lack of expression of kDEF1 in normal inflorescence. d, Sequences of primers diagrammed in panel b. e–f, PCR amplicons including each qRT-PCR amplified sequence were serially diluted and quantified in triplicate by qPCR using the indicated primer pairs. Dilutions (x-axis) were plotted against the measured cycle threshold (y-axis). e, Standard curves for cDEF1 (blue), kDEF1 (red) and tDEF1 (green). Line equations were used to calculate the efficiency of each primer pair. The efficiency of each primer pair was used in calculations for quantification of expression of each associated transcript. f, Standard curves for two endogenous oil palm control genes. The efficiency of each primer pair was used in calculations for quantification of expression of each associated transcript. Expression of each alternative transcript was calculated relative to the control PD00569 control. Control qRT-PCR primers are described in Chan et al.39.