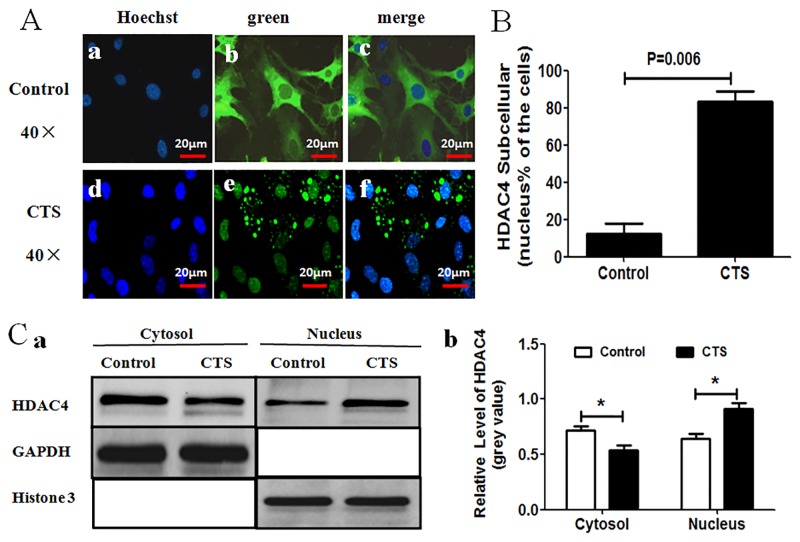
Fig 2. CTS-induced HDAC4 nuclear relocation in chondrocytes.
(A) Fluorescence microscope showed that GFP-HDAC4 was mainly located in the cytoplasm of cells in non-stretched control group (a-c), while GFP-HDAC4 was relocated to nucleus of cells subjected to CTS (d-f). Green indicated the GFP-HDAC4 and blue indicated cell nuclei stained by Hoechst 33342. (B) Percentage of GFP-HDAC4 located in nucleus was scored. 300 cells from 3 independent experiments were counted. Data were expressed as means±SD (P = 0.006). (C) Nuclear and cytoplasmic lysates were separated and followed by western blot analysis with anti-HDAC4 antibody. Histone 3 and GAPDH acted as loading controls for the nuclear and cytoplasmic fraction respectively (C-a). Semi-quantitative assay of band densities showed that cytoplasmic HDAC4 was decreased, and nuclear HDAC4 was increased in CTS group as compared to non-stretched control group (C-b), Values were presented as mean±SD (n = 3).