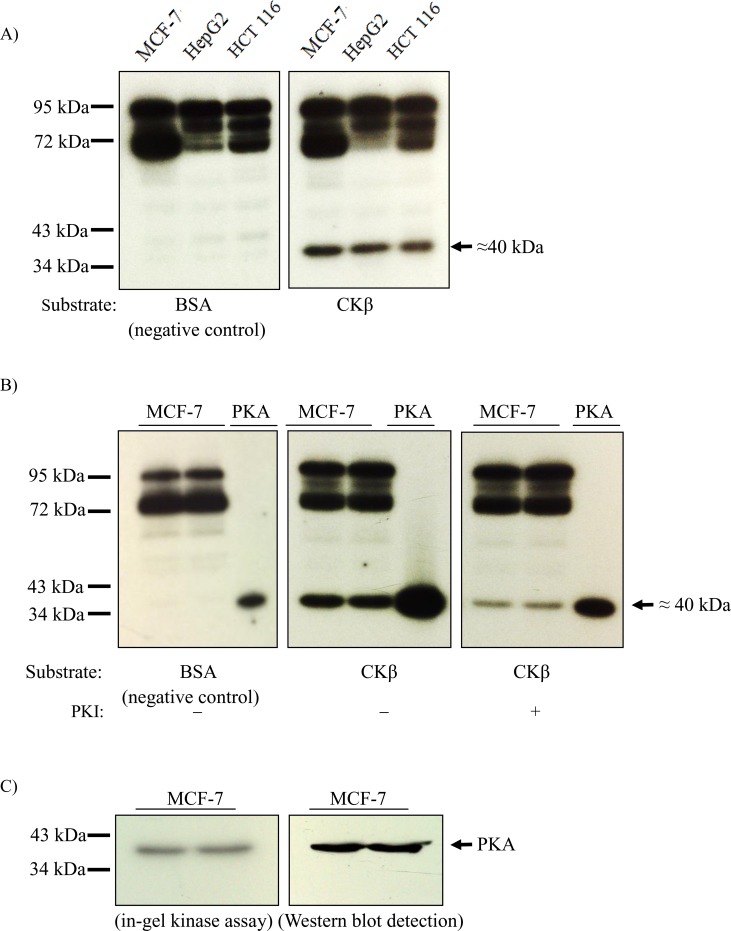
Fig 2. Identification of PKA as the protein kinase responsible for the phosphorylation of CKβ.
A) In-gel kinase assay of CKβ with MCF-7, HepG2, and HCT-116 as the sources of protein kinase PKA. Two milligrams of CKβ were used as phosphorylation substrate in the gel, and 60 μg of cell lysate were applied in each lane. After electrophoresis, the gel was washed, incubated in denaturation and renaturation buffers as described in the experimental procedures, followed by the kinase reaction by incubating the gel with 50 μM of radiolabelled ATP for 4 hours. The reaction was terminated by incubating the gel in stop buffer. CKβ phosphorylation was detected by autoradiography. B) Effect of specific PKA peptide inhibitor (PKI) on the activity of the 40 kDa protein kinase. The in-gel kinase assay was run as described above with 15 μg/mL of PKI included in the kinase buffer. MCF-7 cell lysates were run in duplicate lanes. C) Western blot detection of the 40 kDa protein kinase by a specific anti-PKA antibody. A replicated gel of the in-gel kinase assay before the kinase reaction step was blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane followed by immunodetection with 1:5,000 dilution of anti-PKA catalytic subunit polyclonal antibody.