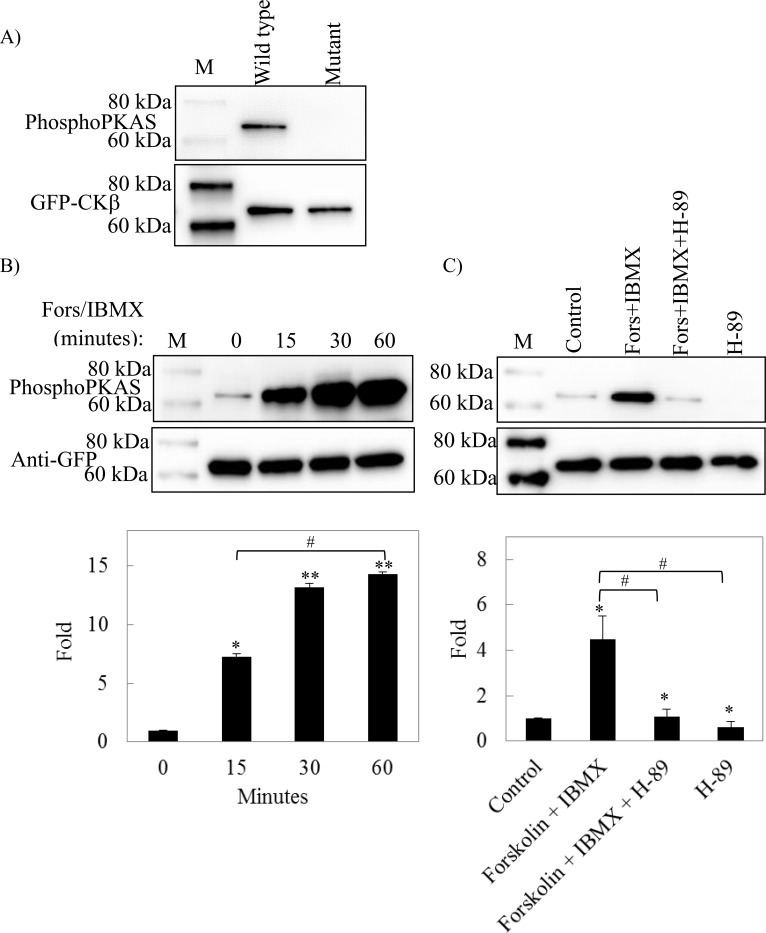
Fig 6. Effect of forskolin, IBMX, and H-89 treatment on the intracellular phosphorylation of GFP-CKβ.
A) Phosphorylation state of the GFP-tagged wild type and S39A/S40ACKβ phosphorylation-negative mutant. B) Time-dependent effect of forskolin (fors) and IBMX treatment on the level of CKβ phosphorylation. C) Effect of H-89 treatment on the level of CKβ phosphorylation. In all experiments, the phosphorylation level of the immunoprecipitated CKβ was monitored by PhosphoPKAS antibody, and anti-GFP antibody detection was subsequently performed as the loading control. The intensities of respective bands were quantitated by Image J 1.42 software and plotted as the phosphorylation level relative to the control. Each bar represents the standard error of the mean (SEM) from two independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA and the Tukey HSD post-hoc test (*p < 0.05 vs control; **p < 0.01 vs control, #p < 0.05, significant between treatment group). M: Supersignal® molecular weight protein ladder.