Fig 2. Phenotype of the 42.49 mutant.
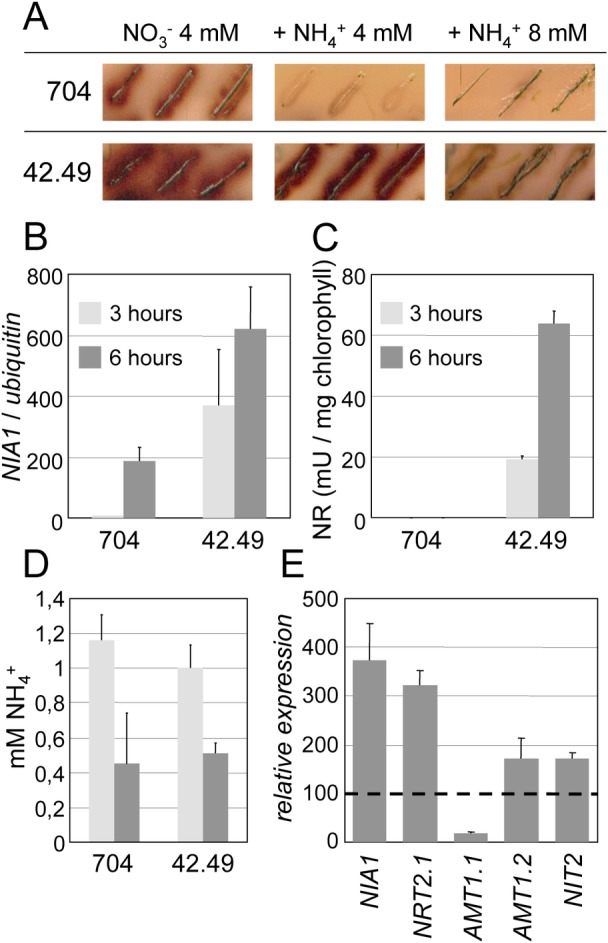
(A) Arylsulfatase (ARS) activity in the parental strain 704 and in the 42.49 mutant after four days on solid medium containing either 4 mM NO3– as the sole nitrogen source, or NO3– supplemented with NH4+ at the indicated concentrations. Both 704 and 42.49 strains bear a copy of the ARS gene fused to the NIA1 promoter, so that ARS activity in the presence of NH4+ reveals that the promoter is not fully sensitive to NH4+ repression. (B) NIA1 transcript abundance was quantified by qRT PCR in 704 and 42.49 strains after 3 and 6 hours in medium containing 4 mM NO3– + 1 mM NH4+. The data were obtained from three technical replicates of two biological samples, and the error bars represent the standard deviation. (C) NR activity was determined in cell extracts of 704 and 42.49 strains in the same conditions than in (B). One mU of enzyme activity corresponds to the reduction of 1 nmol of substrate per minute. These results are representative of three independent biological replicates. (D) The residual concentration of NH4+ that remained in the medium was determined in parallel to the NR activity assay described in (C). (E) In an independent experiment from (B), transcript abundance of NIA1, NRT2.1, AMT1.1, AMT1.2 and NIT2 was determined in 704 (wt) and 42.49 after 6 hours in medium containing NO3−4 mM and NH4+ 1 mM. Results are expressed in % relative to the wild type. The presence of NH4+ was checked but not quantified.
