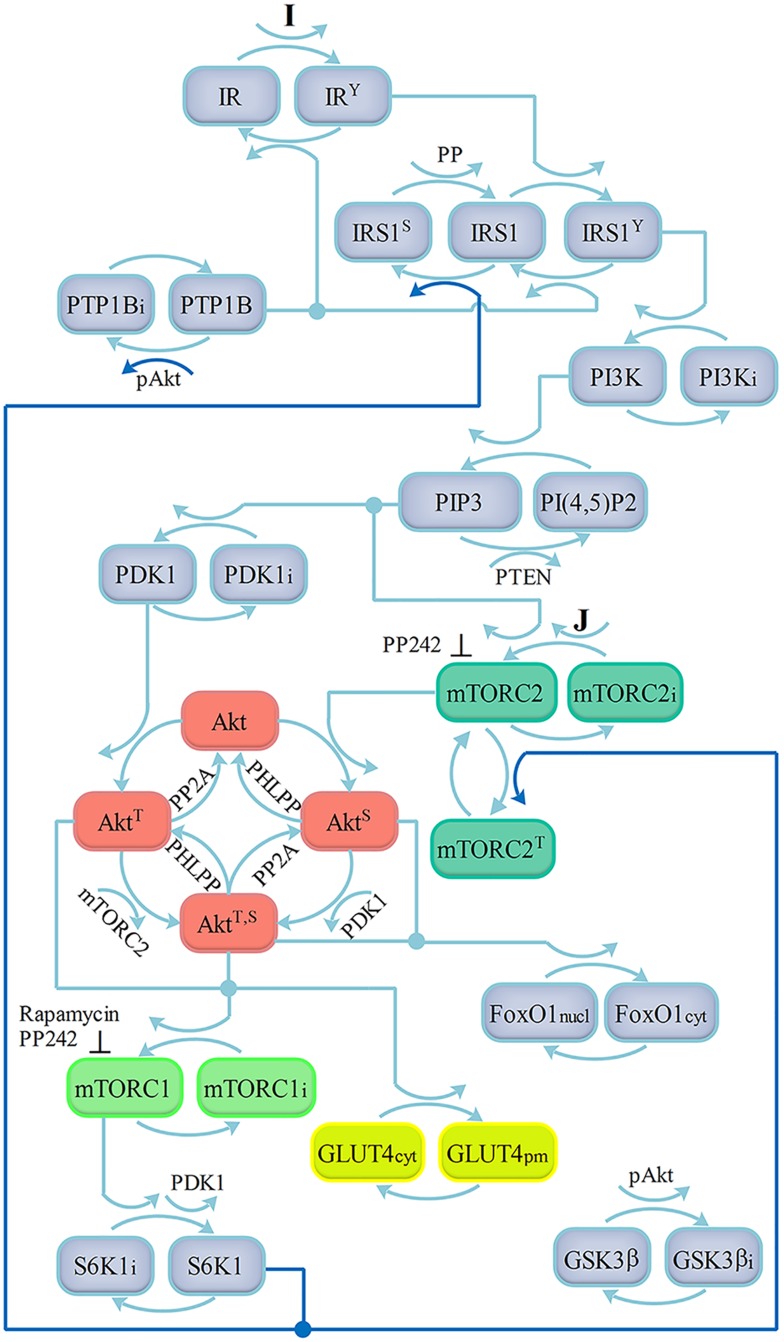
Fig 1. Scheme of the insulin signaling network.
Activation by insulin (I) of insulin receptor (IR) catalyzes tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS1. Phosphorylated IRS1 binds the p85 regulatory subunit of PI3K, activating the p110 catalytic subunit. PI3K mediates phosphorylation of PI(4,5)-bisphosphate (PIP2) to PI (3,4,5)-trisphoshpate (PIP3) near plasma membrane (PM) and the phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) dephosphorylates PIP3 back to PIP2. PIP3 recruits Akt and PDK1 to PM, where PDK1 phosphorylates Akt at Thr308 (phosphatase PP2A). mTORC2 is activated by PIP3 and by the factor J, and catalyzes Akt phosphorylation on Ser473 (phosphatase PHLPP). Maximal Akt activity is achieved when the molecule is phosphorylated on both Thr308 and Ser473 residues, allowing translocation of GLUT4 glucose transporters to PM. GSK3 and FoxO1 are direct Akt substrates. Akt also activates mTORC1, which in turn activates S6K1. Activated S6K1 phosphorylates IRS1 and Rictor in negative feedback loops. The positive feedback loop from Akt to PTP1B is also included. Feedback loops are represented by bold lines.