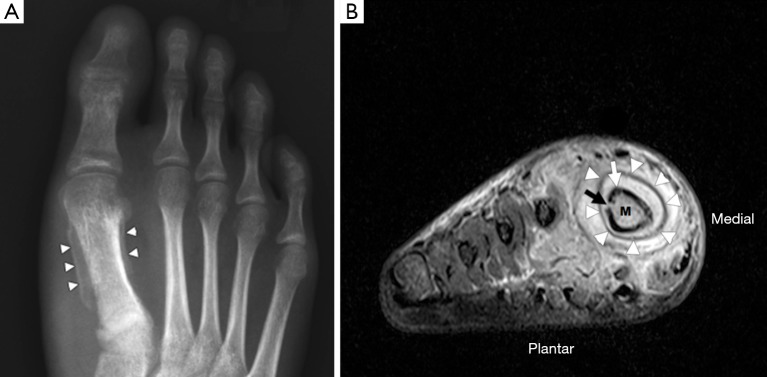
Figure 2.
Osteomyelitis in the right foot of a 63-year-old male. (A) The dorso-plantar radiograph shows a periosteal reaction around the 1st metatarsal diaphysis (white arrowheads); (B) short axis coronal short-tau inversion recovery (STIR) image of the same patient demonstrating marked soft tissue oedema surrounding the 1st metatarsal. The periosteum (white arrowheads) is separated from the cortex (white arrow) by high signal material representing pus. There is a defect in the cortex (black arrow), known as a cloaca, that allows pus to drain from the medullary cavity into the subperiosteal space. Compared to the other metatarsals, the medulla (M) of the 1st metatarsal has high signal, consistent with bone marrow oedema.