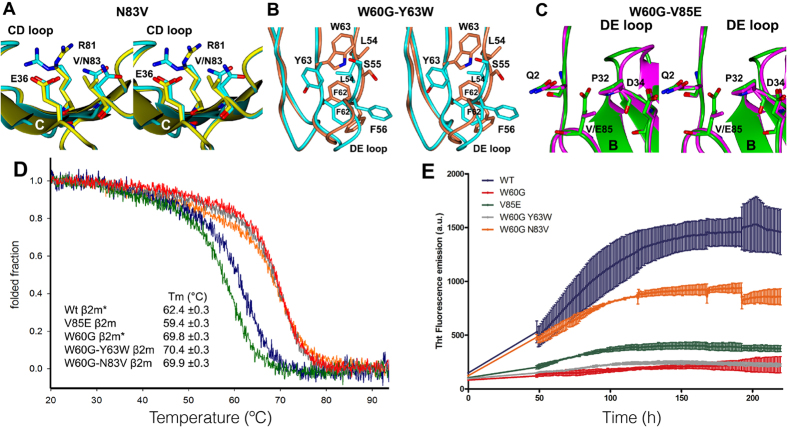
Figure 5. Structure, stability and aggregation of the β2m variants.
(A) The superimposed structures of the W60G and W60G-V83N mutants are shown in cyan and yellow, respectively. (B) Zoom of the (D and E) strands: the superposed structures of the W60G and W60G-Y63W are shown in cyan and coral, respectively. (C) Superimposed structures of wild-type β 2m and the V85E variant, at the mutation site, shown in magenta and green, respectively. (D) Thermal unfolding of wild-type β 2m, of the W60G variant and of the three surface mutants, monitored by far-UV CD at 202 nm. In the table the measured Tm are reported (*the Tm of wild-type and W60G variants have been previously reported23). (E) Comparison of the kinetics of fibril formation of the various mutational variants of β 2m analyzed in this work monitored by fluorescence in a thioflavin T assay.