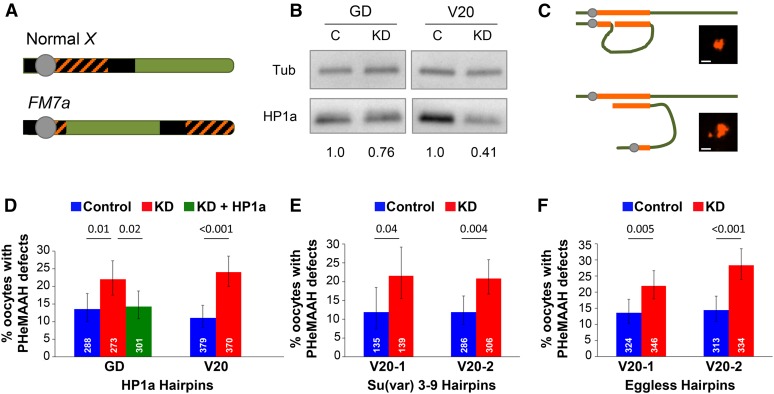
Figure 1.
Reduction of HP1a protein or H3K9 methyltransferases in FM7a/X oocytes disrupts PHeMAAH. (A) Diagram of wild-type Drosophila X chromosome and its derivative, the FM7a balancer. Heterochromatin is shown as black. Orange cross-hatching denotes the 359-bp satellite DNA repeats recognized by the FISH probe. The centromere is the gray circle. Rearrangements within the FM7a euchromatin (green) suppress recombination with a normal X chromosome. (B) Immunoblots of ovary extracts from HP1a knockdown (KD) and control (C) flies. The relative intensity of HP1a signal for each set of knockdown and control extracts is shown below the blot. For each lane, HP1a signals were normalized to tubulin. GD and V20 correspond to the HP1a hairpins used for knockdown. (C) Schematic diagram of heterochromatic pairing between FM7a and a normal X chromosome. Pairing between euchromatic regions has been omitted for clarity. The 359-bp repeats are shown in orange. When PHeMAAH is normal (top), association between heterochromatic regions results in one large, visible FISH signal. When PHeMAAH is disrupted (bottom), the pericentric regions separate, resulting in one small dot corresponding to the FM7a pericentric region and one large dot representing the remaining 359-bp repeats of the FM7a and normal X chromosomes. Inset images show representative oocyte FISH signals. Scale bars, 1.0 µm. See Materials and Methods for other heterochromatin pairing configurations not shown. (D–F) Levels of FM7a/X PHeMAAH defects measured by FISH. P-values are shown above the bars, and 95% confidence intervals are presented as error bars. Number of oocytes assayed for each genotype is indicated in white. Control flies carry the UAS hairpin transgene but lack the matα driver, so the hairpin is not expressed. KD flies express the hairpin under the control of the matα driver (see Materials and Methods). Complete data for these experiments are provided in Table S3. (D) In HP1a RNAi experiments, 60 ovarioles were scored for each genotype using the GD hairpin, and 90 ovarioles were scored for each V20 hairpin genotype. (E) In Su(var)3–9 RNAi experiments, 30 and 60 ovarioles were scored for each genotype containing the V20-1 and V20-2 hairpins, respectively. (F) For both Eggless hairpins, 60 ovarioles were scored for each genotype.