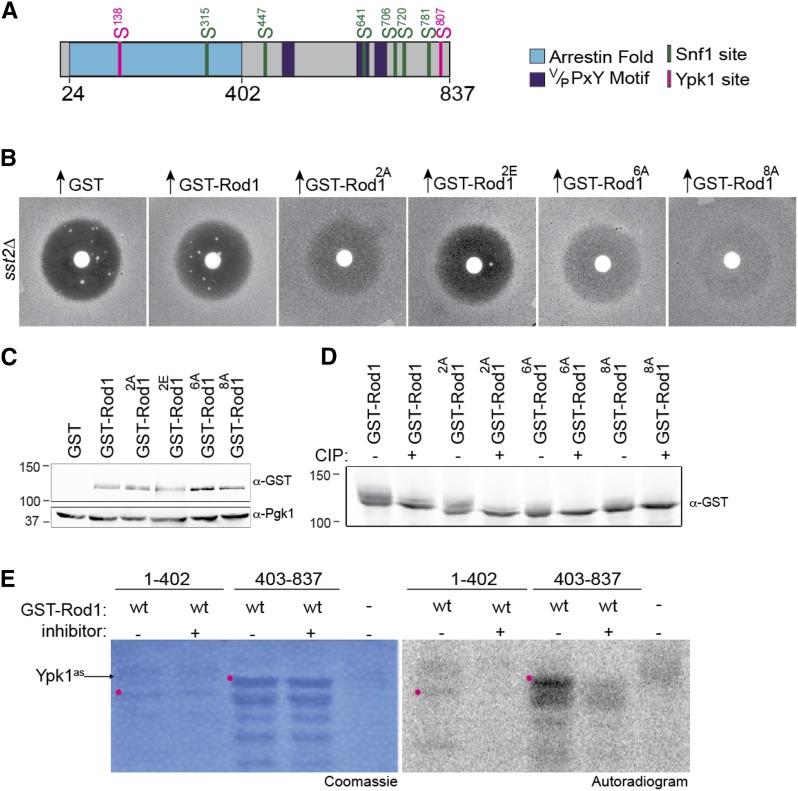
Figure 2.
Ypk1 phosphorylates Rod1 in vivo and in vitro. (A) Schematic diagram of Rod1. Arrestin fold (blue); Rsp5-binding motifs (purple); six Snf1 consensus motifs (green); two Ypk1 consensus motifs (pink). (B) The adaptation-promoting capacity of the indicated alleles of Rod1 was assessed as in Figure 1A. 2A, Rod1(S138A S807A); 2E, Rod1(S138E S807E); 6A, Rod1(S315A S447A S641A S706A S720A S781A); 8A, Rod1(S138A S315A S447A S641A S706A S720A S781A S807A). (C) Expression of the Rod1 variants shown in B was assessed by harvesting the indicated cultures just prior to plating, preparing whole-cell extracts, resolving samples of those lysates by SDS-PAGE (7.5% gel), and analyzing immunoblots of the resulting gels with anti-GST or anti-Pgk1 (loading control) antibodies. (D) Phosphorylation status of the Rod1 variants shown in B was assessed as described in Figure 1D, except that the SDS-PAGE separation was performed on a 5% gel to exaggerate band shifts. (E) In vitro phosphorylation assay, conducted as in Figure 1E, except that purified Ypk1-as was the protein kinase added, not Snf1, in the absence (−) and presence (+) of the Ypk1-as-specific inhibitor 3-MB-PP1. Position of the indicated full-length GST fragment (red dot).