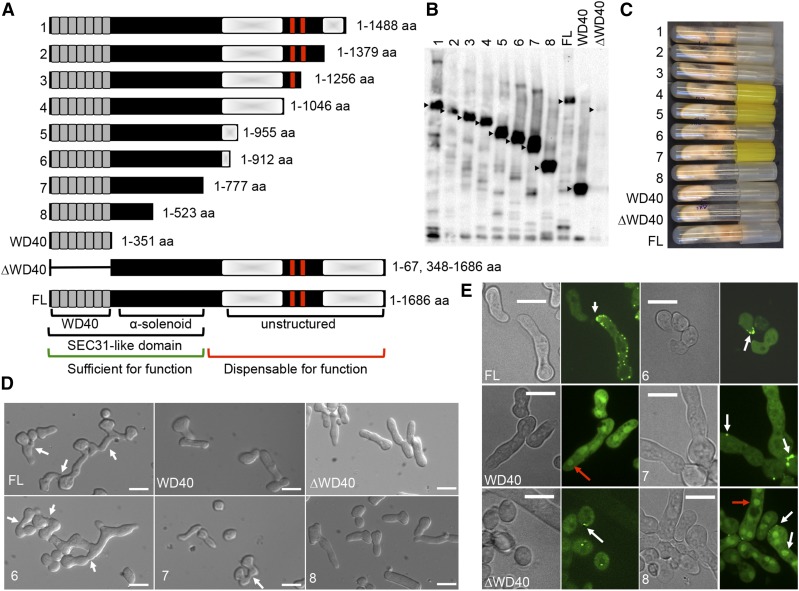
Figure 1.
Phenotypes and functional characterizations of truncated HAM-5–GFP proteins. (A) Schematic overview of the eight different truncated HAM-5 constructs (1–8), WD40 only version (1–351 aa), ∆WD40 version (1–67 and 348–1686 aa) and the full-length (FL) protein (1–1686 aa). The predicted WD40 domains are shown in gray and the putative coiled coil domains are shown as red bars. Shaded white boxes depict the two disordered regions with low complexity. The Sec31-like domain consists of the WD40 and the α-solenoid motifs found in S. cerevisiae Sec31 protein. The region of HAM-5 sufficient for function is marked by a green bar, while the region dispensable for function by a red bar. (B) Western blot of ∆ham-5 germlings bearing the eight different ham-5–gfp truncation constructs, FL ham-5–gfp, the wd40-gfp version (1–351 aa) or the ∆wd40-gfp (1–67 and 348–1686 aa) construct. Samples from 5-hr-old germlings were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibodies. Black triangles point to the HAM-5 protein bands of the correct size in the strains. (C) Growth phenotype of ∆ham-5 strains bearing the eight different truncated ham-5-gfp constructs, the wd40-gfp version, the ∆wd40, and the FL ham-5–gfp version on a Vogel’s minimal medium agar slant. (D) Germling fusion phenotypes of ∆ham-5 germlings bearing FL ham-5–gfp, wd40-gfp, ∆wd40-gfp, or the three shortest truncated ham-5–gfp constructs (constructs 6–8). White arrows point to germling pairs that have fused. Bar, 10 µm. (E) Cellular localization of the FL HAM-5–GFP protein, the WD40-GFP version (Jonkers et al. 2014), the HAM-5∆WD40, and the three shortest truncated HAM-5–GFP proteins (constructs 6–8). White arrows point to HAM-5–GFP puncta, red arrows to HAM-5–GFP accumulation in nuclei. Bar, 10 µm.