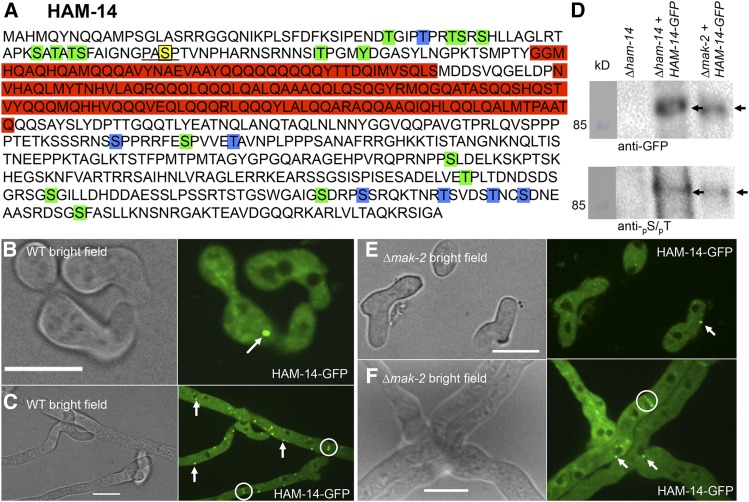
Figure 5.
HAM-14 is a phosphoprotein that localizes to the cytoplasm, occasionally to puncta, and is excluded from the nucleus. (A) Protein sequence of HAM-14. The red boxes represent predicted coiled coil domains. The MAPK phosphorylation site (amino acid S73) is marked by a yellow box and underlined. The 23 additional phosphorylation sites (T39, T43, T46, S47, S49, S61, S63, T65, S66, S73, T91, Y95, S345, S352, T357, S436, T496, S510, S538, S542, T550, T555, and S558) are marked in blue (Jonkers et al. 2014) and green boxes (Xiong et al. 2014). (B) HAM-14–GFP localizes in the cytoplasm and occasional puncta in communicating germlings (white arrow). Bar, 10 µm. (C) In hyphae, HAM-14–GFP localizes to the cytoplasm, puncta (white arrows), and septa (white encircled). Bar, 10 µm. (D) Top shows a Western blot of protein samples from germlings of ∆ham-14, ∆ham-14; his-3::ham-14-gfp, and ∆mak-2; his-3::ham-14-gfp strains (Table S1), which were subjected to immunoprecipitation and Western blotting with anti-GFP antibodies (black arrow, 93 kDa). Bottom shows a Western blot of identical anti-GFP immnoprecipitated samples probed with an antibody that specifically detects phosphorylated serine or threonine residues (black arrow) (E) HAM-14–GFP localizes in ∆mak-2 germlings to the cytoplasm and occasional puncta (white arrow). Bar, 10 µm. (F) HAM-14–GFP localizes in ∆mak-2 hyphae to the cytoplasm, occasional puncta (white arrows), and septa (white encircled). Bar, 10 µm.