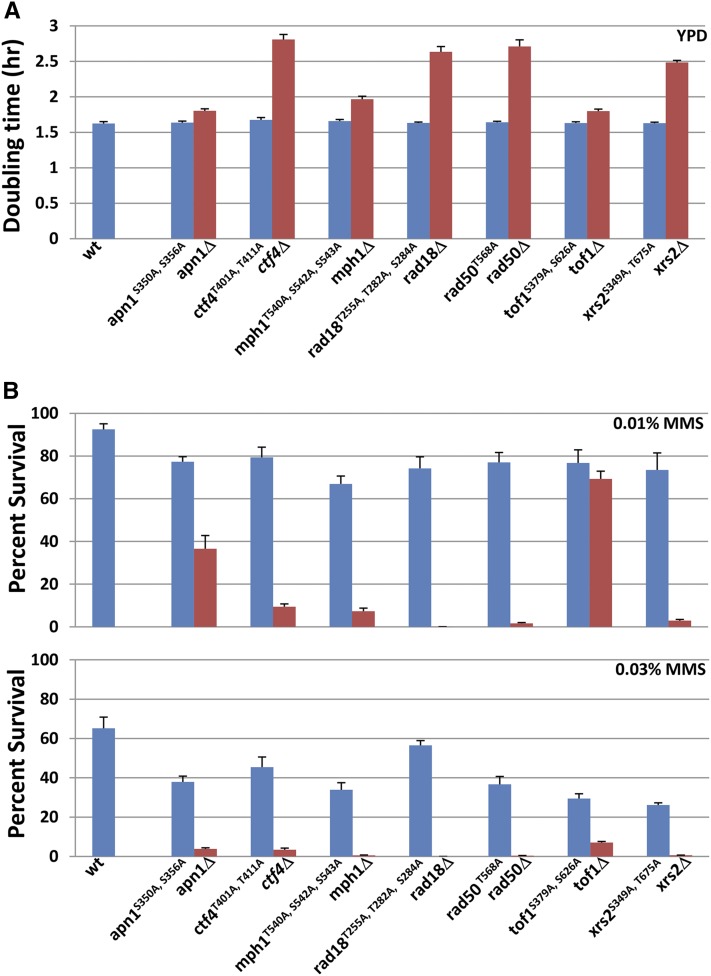
Figure 2.
Nonphosphorylatable alleles show mild but significant dose-dependent MMS sensitivity. (A) Doubling times of various phospho-mutants as compared to their respective deletion strains. Log-phase cultures were diluted in YPD such that all cultures started at a density of 5 × 105 cells/ml. The cell density of each culture was subsequently measured every 2 hr for 10 hr. The log numbers were then plotted. The doubling times were calculated from determining the slope of the straight line of each graph after linear regression. Three independent, sequence-verified isolates of each genotype were assayed, and the error bars represent the standard deviation for the three isolates. (B) Cell survival in two doses of MMS. For quantitative survival analyses in MMS, log-phase wild-type, nonphosphorylatable point mutants and deletion mutants were serially diluted in PBS and spread onto YPD, YPD + 0.01% MMS, or YPD + 0.03% MMS plates. Viable cells were determined by the number of CFUs after 3 days at 30°. Three independent sequence-verified, independent transformants of each strain were tested, and the error bars represent the standard deviation for the three isolates. Of note, a rad18Δ strain is highly sensitive to MMS so that zero CFUs were obtained from a 0.03% MMS plate.