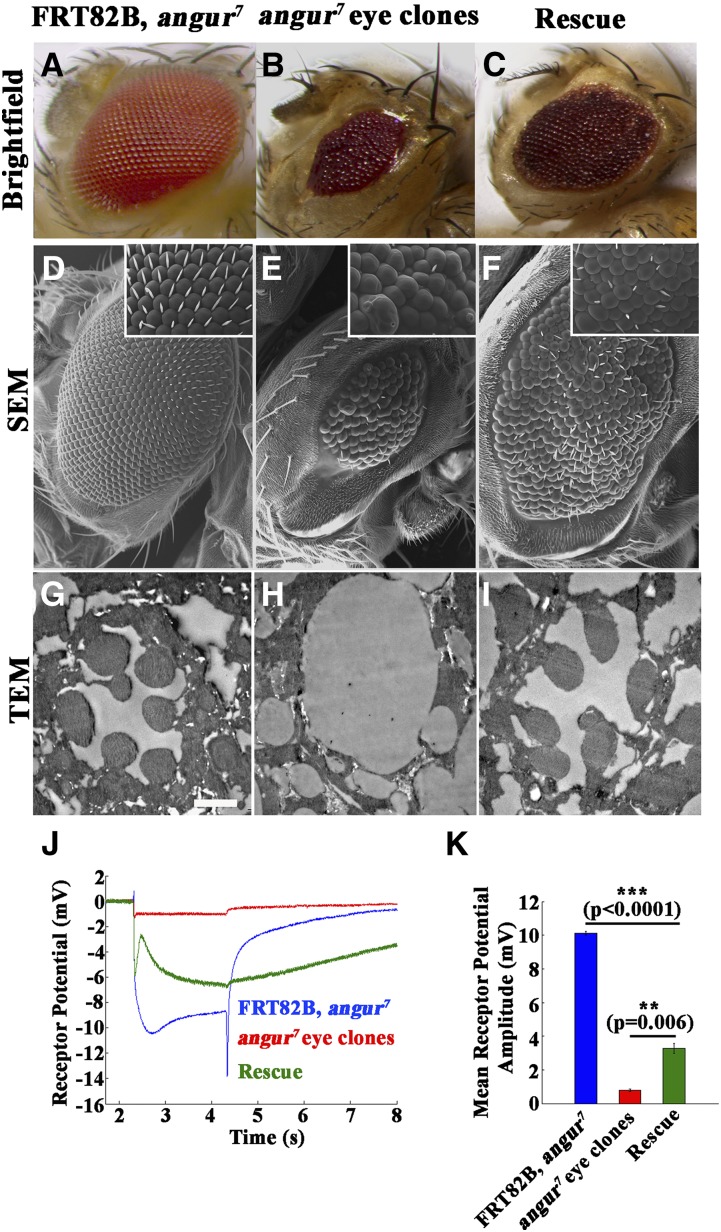
Figure 2.
angur mutant eye clones show severe defects in rhabdomere development. (A–C) Brightfield images of (A) control (FRT82B, angur7), (B) mutant angur7 eye clone (EGUF/+; FRT82B, angur7/FRT82B, GMR-hid), and (C) transgene-rescued animal (EGUF/+; FRT82B, angur7, UAS-AP2σ/FRT82B, GMR-hid). (D–F) SEMs of (D) control (FRT82B, angur7), (E) mutant angur7 eye clone (EGUF/+; FRT82B, angur7/FRT82B, GMR-hid), and (F) transgene-rescued animal (EGUF/+; FRT82B, angur7, UAS-AP2σ/FRT82B, GMR-hid). (G–I) TEMs of (G) control (FRT82B, angur7), (H) mutant angur7 eye clone (EGUF/+; FRT82B, angur7/FRT82B, GMR-hid), and (I) transgene-rescued animal (EGUF/+; FRT82B, angur7, UAS-AP2σ/FRT82B, GMR-hid). Scale bar, 2 μm. (J) ERG traces of control animals (FRT82B, angur7) shown in blue, mutant angur7 eye clone animals (EGUF/+; FRT82B, angur7/FRT82B, GMR-hid) shown in red, and transgene-rescued animal (EGUF/+; FRT82B, angur7, UAS-AP2σ/FRT82B, GMR-hid) shown in green. (K) Histogram showing quantification of receptor potential amplitudes of the preceding genotypes. ***P < 0.0001. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. Statistical analysis based on one-way ANOVA followed by post-hoc Tukey’s multiple-comparison test. Note that compared to the mutant eye clones, the rescued animals showed mild but significant rescue of receptor potential depolarization.