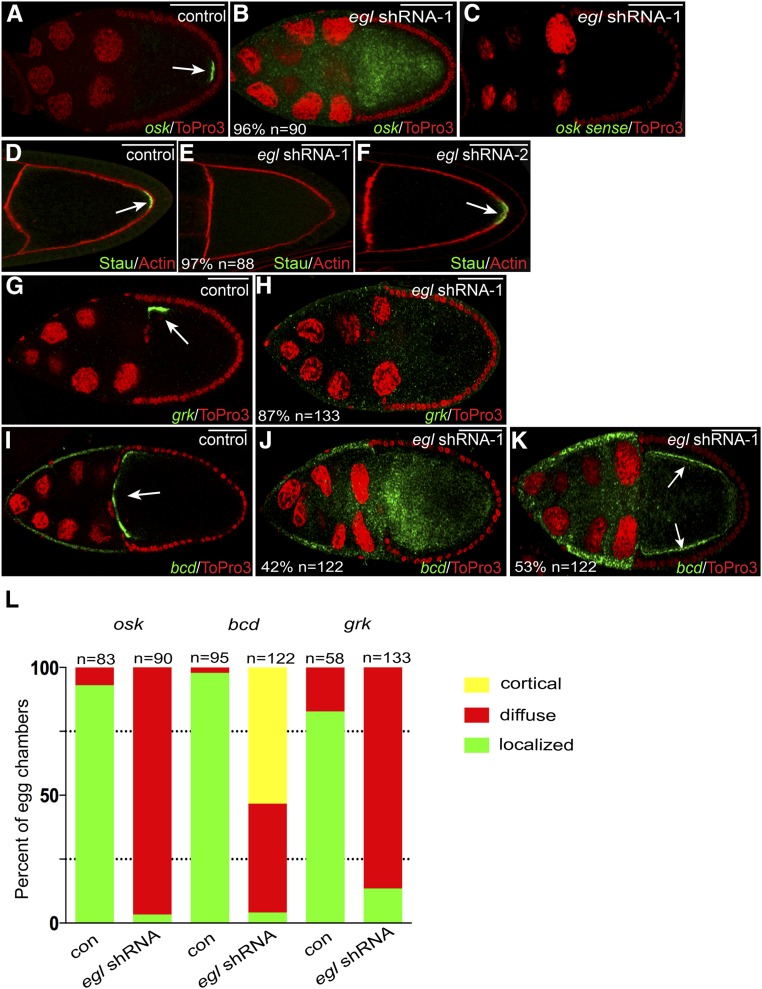
Figure 3.
mRNA localization defects in Egl-depleted egg chambers. (A and B) Egg chambers expressing either a control shRNA (A) or egl shRNA-1 (B) using the early-stage driver were fixed and processed for in situ hybridization using an antisense probe against osk mRNA (green). The egg chambers were counterstained with ToPro3 to reveal nuclei (red). The arrow in A indicates the normal localization of osk mRNA at the posterior pole. (C) To examine the specificity of the in situ hybridization signal, ovaries from egl shRNA-1-expressing flies were fixed and processed for in situ hybridization using a sense probe against osk mRNA (green). The egg chambers were also counterstained with ToPro3 (red). (D–F) Egg chambers expressing a control shRNA (D), egl shRNA-1 (E), or egl shRNA-2 (F) were fixed and processed for immunofluorescence using an antibody against Staufen (Stau, green). The egg chambers were also counterstained with phalloidin to reveal F-actin (red). The arrows in D and F indicate the posterior localization of Stau in control and egl shRNA-2-expressing egg chambers. Also indicated in E is the penetrance of the phenotype and the number of egg chambers that were scored. (G and H) Egg chambers expressing a control shRNA (G) or egl shRNA-1 (H) using the early-stage driver were fixed and processed for in situ hybridization using an antisense probe against grk mRNA (green). The samples were counterstained with ToPro3 (red). The arrow in G indicates the normal localization of grk mRNA at the dorsal–anterior corner of the oocyte. (I–K) The same two strains used in the above panels were also examined using an antisense probe against bcd mRNA (green). ToPro3 was used to visualize nuclei (red). The arrow in I indicates the normal localization of bcd mRNA at the anterior margin of the oocyte. In 42% of egg chambers expressing egl shRNA-1, bcd mRNA was delocalized throughout the entire egg chamber (J). In 53% of egg chambers expressing egl shRNA-1, bcd mRNA accumulated along the cortex (K, arrows). (L). The graph represents quantification of mRNA localization phenotypes. The two strains analyzed were ones expressing either a control shRNA or egl shRNA-1 using the early-stage driver. The green bars represent a wild-type localization pattern (examples in A, G, and I). The red bars represent egg chambers containing mRNA that was diffusely distributed throughout the entire egg chamber (examples are B, H, and J). The yellow bar represents mRNA that was detected along the cortex (K). The number of egg chambers scored for each genotype is indicated. Bar, 50 μm.