Fig. 1.
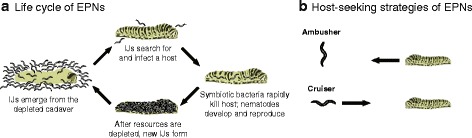
Life cycle and host-seeking strategies of entomopathogenic nematodes (EPNs). a The EPN life cycle. Infective juveniles (IJs) search for hosts in the environment. Once a host is identified, IJs infect the host and release endosymbiotic bacteria harbored in their gut, which rapidly kill the host [48]. IJs then resume development and reproduce until resources are depleted, at which point new IJs form and emerge from the host cadaver to search for new hosts. Adapted from Hallem et al. [22]. b Host-seeking strategies of EPNs. Ambushers wait for hosts to approach; cruisers migrate through their environment in search of hosts [21]
