Fig. 2.
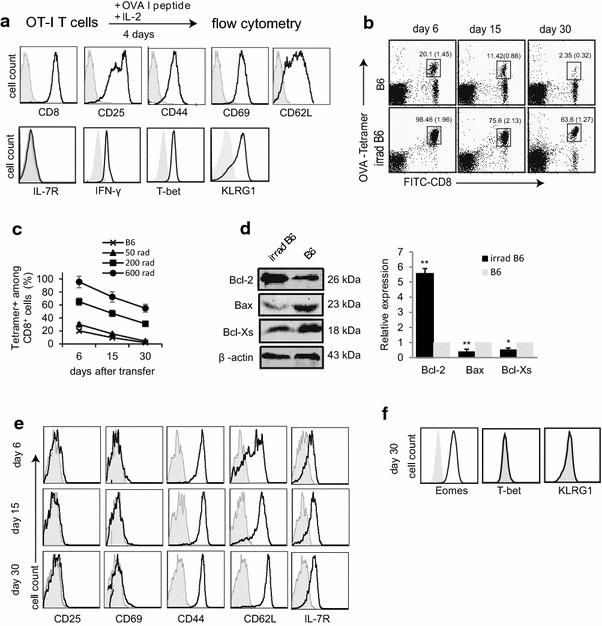
Irradiation-induced lymphopenia promotes survival and memory formation of transferred effector T-cells. a In vitro OVA-I peptide/IL-2 stimulated OT-I CD8+ T-cells were stained with various Abs (solid lines) and analyzed by flow cytometry. Gray shaded histograms represent isotype Ab controls. b Blood samples in WT B6 or irradiated (600 rads) B6 mice (n = 4) were collected and stained with PE-Kb/OVA I-tetramer (OVA-tetramer), FITC-anti-CD8 Ab (FITC-CD8), and analyzed by flow cytometry at indicated times after T-cell transfer. The values represent the percentages of OVA-specific CD8+ T-cells in total CD8+ T-cell population. The values in parenthesis represent SD. c Kinetic assessment of transferred CD8+ T-cells in B6 mice irradiated with different doses by cytometry as described in (b). d Western blot analysis. Transferred T-cells were purified from WT B6 and irradiated (600 rads) B6 mice 6 days after T-cell transfer, and lysed for Western blot analysis. Relative expression represents the ratio of expression of each molecule in cells from irradiated B6 mice versus that in untreated control WT B6 mice. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. e, f Blood samples in irradiated (600 rads) B6 mice were collected and stained with PE-Kb/OVAI-tetramer, FITC-anti-CD8 Ab and PE-Cy5-Abs specific for various molecules, and analyzed by flow cytometry at indicated times after T-cell transfer. The double positive (OVA-tetramer and CD8) T-cells were gated as in Fig. 2b for assessing the expression of CD25, CD69, CD44, CD62L and IL-7R (solid lines). Gray shaded histograms represent isotype Ab controls. One representative experiment of two is shown
