Fig. 6.
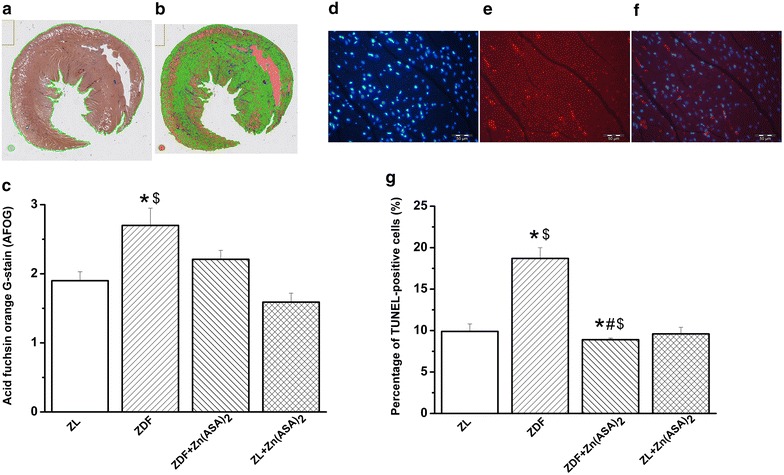
Effect of Zn(ASA)2 on myocardial fibrosis and DNA-strand breaks in cardiomyocytes. Representative photomicrographs showing the whole-slide after a the region of interest detection and b pixelwise classification of the tissue; blue fibrotic areas, green normal tissue, orange excluded areas in the acid fuchsin orange G (AFOG) stained sections. c Quantitative analysis of interstitial fibrosis in the myocardium. Representative photomicrographs of d nuclei with 4′,6-diamidino-2phenylindole (DAPI-stained nuclei, blue); e nuclei with fragmented DNA visualized by Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase-Mediated dUTP Nick End-Labeling (TUNEL) staining (TUNEL-positive nuclei, red), and f merged image (red/blue double stained) (magnification ×400, scale bar: 50 µm) from the same sample which belong to the ZDF group. g Quantification of TUNEL-positive cells for each group. Values are mean ± SEM, n = 6–10. *P < 0.05 vs ZL, #P < 0.05 vs ZDF, $P < 0.05 vs Zn(ASA)2. Zn(ASA) 2 indicates a zinc complex of acetylsalicylic acid, ZDF Zucker diabetic fatty rats, ZL Zucker lean
