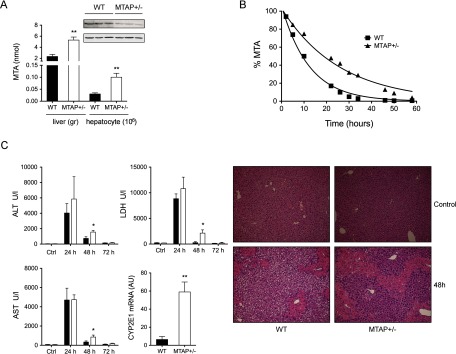
Fig. 6.
Liver sensitivity induced by CCl4 injury in MTAP deficient mice. (A) Characterization of MTAP and MTA level was performed by Western blotting and HPLC analysis, respectively, and showed that a partial deletion of MTAP+-/(40% decrease) in liver mice lead to a twofold increase of MTA hepatic level. (B) In agreement, consumption of exogenous MTA was twofold slower in MTAP± hepatocytes than in WT counterparts. (C) Exposure to a sublethal dose of CCl4 (1 μl/g) induced a more severe damage in MTAP-deficient livers as evidenced by the more extent necrotic area and the larger increase on serum transaminases. Impaired recovery capacity upon 48 h in WT littermates was also observed. Up-regulation of CYP2E1 RNA level may explain the increased sensitivity to CCl4.